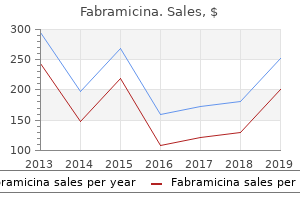
Buy 500 mg fabramicinaThe subdural house forms when a pathologic course of is current antibiotics and beer generic 100 mg fabramicina free shipping, corresponding to a subdural hematoma from trauma/skull fracture and damage of large veins antibiotics for acne worth it order fabramicina 500mg with visa, inflammatory/infectious illness treatment for uti burning buy fabramicina with a mastercard, or neoplasm antibiotics give uti quality 500mg fabramicina. Unlike the epi- and subdural compartment, the subarachnoid area exists without the presence of a pathologic process. The presence of extravascular blood within the subarachnoid house normally is related to a ruptured intracranial aneurysm, vascular malformation, or trauma. Contrast enhancement of the dura can occur because of various causes, including neoplasms (primary and metastatic); inflammation/infection; and benign dural fibrosis secondary to intracranial surgery, transient hypotension (secondary to lumbar puncture), or evolving subdural hematoma. The dural enhancement follows the inside contour of the calvaria without extension in to the sulci. Contrast enhancement in the intracranial subarachnoid house (leptomeninges) is nearly at all times related to vital pathology (inflammation and/or an infection vs neoplasm). Inflammation and/or infection of the leptomeninges may finish up from pyogenic, fungal, or parasitic diseases, as well as tuberculosis. Complications of infectious meningitis embody cerebritis, intraaxial abscess, ventriculitis, hydrocephalus, and venous sinus thrombosis/venous cerebral infarction. Lymphoma and leukemia can even lead to an analogous pattern of leptomeningeal enhancement. Rarely, transient leptomeningeal enhancement can happen from chemical irritation resulting from subarachnoid blood. The outermost layer of the dura mater is a richly vascularized layer with elongated fibroblasts and large intercellular areas that comprise arteries and veins; this layer represents the periosteum of the inner desk of the calvaria. An inside layer of the dura arises from the meninx and consists of epithelial cells. The layers of the cranial dura separate at websites the place there are massive venous sinuses. Reflections of dura kind the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli, which provide support of the traditional positions of the cerebrum and cerebellum. A potential space exists between the dura and the arachnoid, referred to because the subdural space. The cranial pia mater is a thin layer adjoining to the surface of the mind extending alongside the sulci. The cranial pia mater contains elastic fibers internally and collagenous fibers peripherally. Thin connective tissue strands and cellular septa prolong throughout the arachnoid membrane to the pia except on the base of the brain, the place the arachnoid membrane and pia are widely separated. The spinal pia mater is thicker and more adherent to the nervous tissue than the cranial pia. The neurocranium is the portion that encloses the mind and consists of the skull base (chondrocranium, endochondral bone formation) and calvarium (membranous bone formation). Chondrocranial bones of the skull base embody the sphenoid bone, many of the occipital bone, petrous bones, and ethmoid bone. Sites the place the chondrocranial bones of the cranium base fuse are referred to as synchondroses. Growth of the calvarium is instantly dependent on growth of the immediately subadjacent dura. The orientation of the dural fibers is related to the position of five chondrocranial constructions of the skull base (both petrous crests, crista galli, and each lesser sphenoid wings). Calvarial bones include frontal bones (two), parietal bones (two), a small portion of the occipital bone, and squamous parts of temporal bones (two). The coronal suture is positioned between the frontal and parietal bones, the sagittal suture between the parietal bones, the lambdoid suture between the parietal and occipital bones, and the metopic suture between the frontal bones. Junction areas where three or more calvarial bones meet are referred to as fontanelles. The largest is the anterior fontanelle, which is positioned between the frontal and parietal bones. The other fontanelles are considerably smaller and embrace the posterior, posterolateral (mastoid), and anterolateral (sphenoid) fontanelles. The measurement of the calvarial portion of the skull is dependent on development of the intracranial contents (brain and ventricles). Patients with micro- cephalic brains have small-sized calvarial vaults, and those with enlarged brains.
Purchase 100mg fabramicina mastercardThe deep facial spaces that abut the exocranial surface of the central skull base are the retropharyngeal space and the perivertebral area and the paired parapharyngeal space antibiotic young living essential oils discount 250 mg fabramicina with mastercard, masticator space antibiotic withdrawal symptoms quality 250 mg fabramicina, carotid house infection fighting foods order generic fabramicina on-line, and parotid area antibiotics effective against e coli buy cheap fabramicina 250 mg line. The optic canal is a round aperture throughout the lesser wing of the sphenoid at its junction with the sphenoid body, which transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery, each of which are contained in a dural sheath. Inferolaterally, the canal is separated from the superior orbital fissure by the inferior root of the lesser wing ("optic strut"). The inferior orbital fissure, which transmits the infraorbital artery, vein, and nerve, is formed by the cleft between the body of the maxilla and the higher wing of the sphenoid bone. The inferior orbital fissure communicates inferiorly with the pterygopalatine fossa. The foramen rotundum empties anteriorly in to the pterygopalatine fossa, which connects laterally with the masticator Skull Base Apertures and Their Content 203 the foramen magnum is bound by the four segments of the occipital bone: the basiocciput anteriorly, the two elements of the exoocciput laterally, and the supraocciput posteriorly. The bones surrounding the foramen magnum function a site of attachment for quite a few ligaments (apical, dental, and alar ligaments, the upper band of the cruciform ligament, the posterior longitudinal ligament, and the tectorial membrane) that stabilize the craniocervical junction. Diseases of the skull base could be intrinsic to the area or have an result on the cranium base from both above or under. All main lesions involving the skull base, with emphasis on intrinsic lesions, are summarized in Table 5. Comments Temporal bone lesions Intrinsic lesions of the cranium base Congenital/developmental lesions Primary cholesteatoma (epidermoid cyst) Intraosseous congenital cholesteatomas are boneexpanding and bone-destructive lesions. In uncommon circumstances, calcifications may be seen, either within or on the periphery of the cholesteatoma. Occipital cephaloceles include cervico-occipital, low occipital (involving the foramen magnum), and high occipital lesions (above the intact foramen magnum). Frontoethmoidal cephaloceles are subdivided in to frontonasal, nasoethmoidal, and naso-orbital cephaloceles. Transethmoidal, sphenoethmoidal, transsphenoidal, spheno-orbital, and sphenomaxillary encephaloceles are kinds of basal cephaloceles. Within the skull base, this lesion is referred to as congenital cholesteatoma; when discovered within the cisterns, the term epidermoid cyst is utilized. A cephalocele is the protrusion of intracranial contents, together with meninges and mind matter, by way of a defect within the cranium base. Cephaloceles may be congenital or acquired secondary to surgical procedure or trauma or due to spontaneous causes. Cephaloceles are mostly found in the midline, on the occiput, cranium base, or vertex. Associated abnormalities are callosal hypogenesis, interhemispheric lipomas, neuronal migration anomalies, colloid cysts, midline craniofacial dysraphisms, hypertelorism, microcephaly, microphthalmos, and hydrocephalus. Cephalocele Inflammatory/infectious situations Osteomyelitis Poorly outlined areas of osteolysis in contiguity with the primary focus of infection. Intracranial extension could lead to cavernous sinus thrombosis, meningitis, epidural or subdural empyemas, cerebritis, and cerebral abscess formation. Skull base osteomyelitis is rare, and most cases come up from contiguous spread of ear infections. Odontogenic cellulitis and abscess may spread in to the suprazygomatic and nasopharyngeal masticator areas, inflicting osteomyelitis of the cranium base. It usually happens in a diabetic or immunosuppressed patient incompletely handled for necrotizing otitis externa. Less frequently, Aspergillus, Salmonella, Staphylococcus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, or Mucormycosis is implicated. En plaque meningiomas grow as a flattened plate or sheet, particularly on the sphenoid ridge, or much less generally at the superior or posterior surfaces of petrous bone. The uncommon intraosseus meningioma is normally sclerotic, often lytic, and can mimic fibrous dysplasia or Paget disease. Most meningiomas are homogeneously hyperdense, some isodense, and a few hypodense compared with grey matter. Cysts, necrosis, and hemorrhage seem as hypodense, nonenhancing areas; 20% reveal psammomatous, nodular, or rimlike calcifications.
Syndromes - Nerve damage
- The skin is closed with sutures (stitches).
- Removal of CSF from a tube that is already in the CSF, such as a shunt or ventricular drain.
- Easy bruising
- If you have diabetes, heart disease, or other medical conditions, your surgeon will ask you to see your doctor who treats you for these conditions.
- Neck pain
- Weekly from 36 weeks to delivery
- Need for more surgery
- Oily skin, or skin problems such as acne
Cheap fabramicina 250 mg overnight deliveryThe study determines the presence or absence of free intraperitoneal fluid virus spreading in us buy discount fabramicina, mainly within the hepatorenal antimicrobial drug resistance discount 250mg fabramicina overnight delivery, splenorenal antibiotic vitamins order fabramicina 500mg with amex, and suprapubic areas can you take antibiotics for sinus infection while pregnant discount fabramicina 100 mg mastercard. Its most important weaknesses are the shortcoming to determine the supply of free intraperitoneal fluid or to detect injuries to the bowel, retroperitoneum, and diaphragm and its accuracy is operatordependent. The presence of free fluid on ultrasound in a hemodynamically unstable affected person is a sign for pressing laparotomy. However, in Clinical Examination the clinical evaluation of blunt abdominal trauma is commonly sophisticated by related gentle tissue contusion, fractures of the lower ribs or pelvis, head accidents with depressed degree of consciousness, and spinal accidents. These circumstances make scientific examination troublesome and unreliable, and significant hollow viscus injuries may be missed with probably deadly consequences. The process may be carried out with the open or percutaneous closed technique; the closed one uses a guidewire method, as in central venous line insertion, and is quicker and less invasive. In addition to the positioning and measurement of solid organ damage, it could give valuable information about the presence of active bleeding or false aneurysms, supplied intravenous distinction has been administered. Angiography: this is an important diagnostic and therapeutic software in chosen instances of abdominal trauma, corresponding to in suspected bleeding from pelvic fractures or advanced liver injuries. Serum amylase and lipase: They could also be helpful laboratory exams for suspected pancreaticoduodenal trauma, though the sensitivity and specificity are fairly low. Trauma ultrasound research ought to be a part of the usual evaluation of all suspected stomach blunt trauma. Hemodynamically unstable patients or these with indicators of peritonitis must be taken to the working room with no delay. The timing of evaluation and management of the accidents of those anatomical areas is essential and might have a serious impact on consequence. Overall, about 70% of blunt liver accidents, about 80% of splenic injuries, and about 90% of renal accidents could be managed nonoperatively. Delayed diagnosis of hole viscus perforation in a clinically unevaluable patient. They are highly suspicious findings, and exploratory laparotomy must be thought of. Missed pancreaticoduodenal injuries are infamous for their pretty silent clinical presentation. Penetrating Abdominal Trauma Introduction the preliminary analysis of penetrating abdominal trauma is normally very completely different from analysis of blunt trauma. Penetrating trauma, especially gunshot wounds, is much extra likely to be related to lifethreatening main vascular accidents than blunt trauma. Knife accidents to the anterior abdomen are associated with vital intra-abdominal injuries in about 50% of sufferers. In gunshot wounds, about 80% of circumstances have major injuries requiring surgical restore. However, if time permits, they should be obtained for all torso gunshot wounds with no exit and in sufferers with suspected spinal or pelvic fractures. In addition, the pericardium ought to be examined in all patients with proximity wounds. Diagnostic laparoscopy has a definitive role within the evaluation of suspected diaphragmatic injuries (see Chapter 4). Clinical Examination Physical examination is often reliable in identifying sufferers with significant intra-abdominal accidents. The physician must remember that patients with a short prehospital time may seem hemodynamically steady despite severe energetic intra-abdominal bleeding, and thus serial examinations are crucial within the initially asymptomatic affected person. Tachycardia and elevated diastolic stress (narrow pulse pressure) are suspicious markers of bleeding, and these patients ought to be re-evaluated each jiffy throughout admission. Very few investigations are needed within the evaluation of penetrating abdominal trauma. Chest x-ray should be obtained in selected patients with stab wounds or gunshot wounds with suspected thoracic involvement. The x-ray might show hemopneumothoraces, an elevated diaphragm, free air under the diaphragm, and foreign bodies. General Management One of crucial targets in managing penetrating abdominal accidents is to keep away from nontherapeutic laparotomies and yet not miss any important injuries. Patients presenting with hemodynamic instability or signs of peritonitis require an emergency operation Abdominal Injury 121 without any delay.
Buy fabramicina once a dayThe dissection can be extended proximally (as for the posterolateral approach to the tibia) antibiotics for dogs buy online cheap fabramicina 100mg free shipping. This strategy supplies excellent publicity to scale back and stabilize the posterior malleolus with a buttress plate; the posterior border of the fibula may additionally be plated treatment for uti medscape order 250mg fabramicina with visa. Incision A 10-cm longitudinal incision is made halfway between the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon antimicrobial for mold cheap fabramicina 100mg with amex. Superficial surgical dissection Deepen the incision in line with the skin incision to enter the fats surrounding the Achilles tendon infection urinaire femme cheap fabramicina 500 mg with visa. Deep surgical dissection Retract the Achilles tendon and retrotendinous fat laterally, exposing the fascia of the deep flexor compartment. The joint capsule on the posterior facet of the ankle joint is incised longitudinally. Structures at risk Sural nerve Short saphenous vein Posterior tibial neurovascular bundle (if straying too far medial on the tibia). Lateral approach to the foot this method gives good access to the os calcis, peroneii and the lateral ligaments of the ankle. Position the affected person is positioned supine with a sandbag underneath the buttock of the affected aspect. Position Lateral or inclined Ankle elevated off the table with a foam block (if lateral) Tourniquet. Incision A curved incision ~12 cm lengthy is made on the lateral aspect of the ankle. The incision begins 4 cm above the tip of the lateral malleolus on the posterior border of the fibula. The posterior border is adopted all the way down to the tip of the lateral malleolus and then the incision is curved in a hockey stick style forwards, passing over the peroneal tubercle parallel to the course of the Landmarks Fibula and the lateral border of tendo Achilles. Incision A 10-cm longitudinal incision is made midway between the fibula and the Achilles tendon. The incision is carried straight down on to bone, particularly on the angle as it overlies the calcaneus. Internervous airplane the internervous aircraft lies between the peroneus tertius tendon (deep peroneal nerve) and the peroneal tendons (superficial peroneal nerve). Take care not to damage the sural nerve because it runs behind the lateral malleolus with the quick saphenous vein. Incise and open the deep fascia in line with the pores and skin incision to uncover the two peroneal tendons. The inferior peroneal retinaculum is incised and the peroneal tendons are uncovered extra totally and mobilized. In the inferior part of the incision, expose the peroneal tendons and retract them inferiorly. Deep surgical dissection the peroneal tendons are mobilized and retracted anteriorly over the distal end of the fibula. The calcaneofibular ligament is recognized and incised transversely to open the capsule of the posterior talocalcaneal joint. To expose the bare lateral surface of the calcaneum, incise the periosteum over its lateral surface and strip it inferiorly by sharp dissection. Deep surgical dissection Partially detach the fats pad that lies in the sinus tarsi by sharp dissection. Detach this origin by sharp dissection and reflect the muscle distally to expose the dorsal capsule of the talocalcaneonavicular joint and extra laterally the dorsal capsule of the calcaneocuboid joint. The three joints are uncovered through a small opening with out a lot retraction, and the wound normally heals nicely because the proximal flap is dissected full thickness and the pores and skin edges are protected throughout retraction. Cervical backbone Anterior method to the cervical backbone Posterior method to the cervical spine. Position the patient is supine on the working desk with a big sandbag beneath the affected buttock. Landmarks Anterior border of sternocleidomastoid Low border of mandible C2�C3 Hyoid bone C3 Thyroid cartilage C4�5 Cricoid cartilage C6.
Order cheap fabramicina on lineThe medical analysis of the stomach in a paralyzed patient may be very troublesome and unreliable bacteria 400x magnification cheap fabramicina on line. Patients with penetrating cervical or thoracic spinal twine injuries might have further investigation by means of endoscopy or swallow research to rule out related aerodigestive accidents infection of the brain generic 250 mg fabramicina amex. All penetrating accidents to the stomach in paralyzed sufferers should undergo exploratory laparotomy antibiotics for uti when pregnant purchase fabramicina 250 mg amex, because the abdomen is clinically unevaluable antimicrobial yoga towel discount generic fabramicina uk. The management of penetrating cord accidents is usually supportive and operative intervention has little or no role. Similarly, victims with incomplete twine injuries and a missile lodged in the spinal canal could benefit from operative removal. In chosen instances with in depth surrounding edema or shock wave harm because of high velocity missiles, some physicians would possibly give steroids. Patients with complete spinal wire transection at this stage die within a few minutes due to full respiratory muscle paralysis. This affected person, in addition to the quadriplegia, suffered extreme hypoxic mind injury. Cutaneous burns vary from inconsequential superficial accidents that can heal with out medical intervention to overwhelming skin loss and patient death. The extent of the burn depth and measurement is directly associated to the diploma of fluid loss and the extent of the systemic inflammatory response. Patients require careful fluid resuscitation for this blended hypovolemic and hyperdynamic state. In the United States, burns account for about 40�50,000 admissions per year with 80% of sufferers being candidates for outpatient remedy. The American Burn Association has devised specific referral criteria for transfer to specialised burn centers, which have been shown to lower mortality and improve useful consequence of patients. Burn mortality has decreased drastically over the previous three many years on account of early excision and grafting, management of sepsis, advances in ventilatory and nutritional help, and wound care adjuncts corresponding to synthetic skin substitutes. Therefore a centered examination is important to decide the risk of neurologic or musculoskeletal damage. The affected person should be utterly uncovered to assess for the extent of burn, and for evidence of any related trauma. Proper initial resuscitation is dependent on accurate evaluation of both the extent and depth of burn. Percentage of physique surface space involved may be estimated by applying the "Rule of Nines" or the Lund� Browder chart for second-degree or higher burns. In this calculation, the pinnacle and each upper extremity is 9%, while the lower extremities, the anterior and posterior trunks are every 18% of the physique floor space. The decrease extremities are 14% each with the remaining distribution the identical as adults. In the first 24�48 hours the extent of burn measurement and depth is most likely not clear because the harm progresses. Deeply burned pores and skin looses elasticity and manifests as a loss of compliance in response to underlying tissue swelling. Though the initial chest radiographs could also be regular in early inhalation damage, it might demonstrate parenchymal abnormalities such as pulmonary edema. These procedures may be carried out at the bedside to additional evaluate the airways of patients with suspected inhalation damage. Visualization of airway erythema, edema, carbonaceous sputum, and singed nostril hair all signify inhalation harm. Extensive burns of the extremities and subsequent edema make peripheral pulses troublesome to palpate, and Doppler stethoscope may assist detect weak pulses. Whenever suspected, goal measurements can help in further medical administration. Glycemic management can scale back osmotic diuresis and infectious complications, and may improve survival.
100mg fabramicina amexDeep surgical dissection the lower part of the origin of soleus from the fibula is detached and retracted posteriorly liquid antibiotics for sinus infection buy generic fabramicina pills. Develop a plane between the gastrocnemius�soleus teams posteriorly and the peroneal muscle tissue anteriorly antibiotics zithromax purchase 250 mg fabramicina with mastercard. By following the interosseous membrane to the lateral border of the tibia infection after miscarriage discount 500 mg fabramicina otc, the origin of tibialis posterior from the interosseous membrane may be detached and retracted posteriorly to expose the posterior floor of the tibia antimicrobial vs antibiotics order fabramicina 250 mg with amex. Deep surgical dissection Incise the remaining soft tissues longitudinally to expose the anterior floor of the distal tibia and anterior capsule of the ankle joint. Incise the joint capsule longitudinally in line with the pores and skin incision as required. This method can if necessary be extended proximally to expose buildings within the anterior compartment. Distal extension to the dorsum of the foot is possible but could be very hardly ever required. Alternatively, the incision could additionally be curved medially at its distal extent and the tibialis anterior retracted laterally to expose the distal tibia. Structures at risk the short saphenous vein may be damaged when mobilizing the skin flaps. Foot and ankle Anterior method to the ankle Approach to the medial malleolus Approach to the lateral malleolus Posteromedial approach to the ankle Lateral strategy to the foot Lateral method to the tarsus. Structures at risk Cutaneous branches of the superficial peroneal nerve run close to the line of the pores and skin incision. Anterior tibial artery and deep peroneal nerve are in danger with superficial surgical dissection. Position Supine on the operating desk Tourniquet with exsanguination limb draped. Tibialis anterior Extensor Hallucis 524 Chapter 23: Surgical exposures oral core topics Artery Nerve Extensor digitorum Peroneus tertius. The evertor tendons peroneus longus and peroneus brevis (superficial peroneal nerve) move behind the lateral malleolus. There is a basic story a quantity of years ago of a candidate who was proven various colour pictures of the anatomy of the front of the ankle and asked to name various constructions. These colour footage have been being quickly flashed within the path of the candidate from a laptop computer computer by an eminent professor of orthopaedic surgery. Structures in danger Anteriorly the saphenous nerve, which, if reduce, might kind a painful neuroma and cause numbness over the medial side of the dorsum of the foot. Tall Doctors Are Never Happy Approach to the medial malleolus Both anterior and posterior approaches to the medial malleolus can be used. Tibialis Posterior Flexor Digitorum Longus Artery Nerve Flexor Hallucis longus Incision the anterior method consists of a longitudinal curved incision on the medial side of the ankle with its midpoint simply anterior to the tip of the medial malleolus. The incision begins 5 cm proximal to the medial malleolus and then curves forwards to finish anteriorly and distal to the malleolus. The posterior strategy involves a 10-cm incision on the medial side of the ankle, beginning 5 cm above the ankle on the posterior border of the tibia, curving the incision downwards following the posterior border of the medial malleolus. The incision is curved forwards under the medial malleolus to finish 5 cm distal to it. Position the patient is positioned supine on the working desk, with a sandbag beneath the buttock. Landmarks the subcutaneous surface of the fibula and lateral malleolus are palpated. The short saphenous vein runs along the posterior border of the lateral malleolus. Internervous aircraft No true internervous airplane exists but the method is safe as a outcome of the incision cuts down on to subcutaneous bone. Incision A longitudinal incision is made along the posterior margin of the fibula all the greatest way to its distal end. Identify and protect the saphenous nerve and long saphenous vein, which lie anterior to the medial malleolus.
Coleus barbatus (Forskolin). Fabramicina. - How does Forskolin work?
- Use by injection for congestive heart failure (CHF).
- Asthma, when inhaled (breathed in).
- Use by injection for a heart condition called idiopathic congestive cardiomyopathy.
- What is Forskolin?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96999

Order 500 mg fabramicina free shippingAssociated larger tuberosity (in anterior dislocation) or lesser tuberosity (in posterior dislocation) fractures or proximal humerus fractures or glenoid rim fracture and Hill�Sachs lesion antibiotics kill probiotics purchase 500 mg fabramicina overnight delivery. Lateral end of clavicle fracture Direct harm � fall on to shoulder antibiotic resistance uptodate purchase fabramicina 500 mg otc, contact sports Assessment � local soft-tissue status virus jamaica generic fabramicina 500mg on line, tenting of pores and skin antibiotics for acne ireland cheap 250 mg fabramicina with amex, distal neurovascular standing, remainder of shoulder girdle. Anatomical considerations Static restrictions for shoulder joint dislocation: Glenoid shape and labrum Glenohumeral ligaments �superior and coracohumeral ligaments � limits exterior rotation in adducted shoulder Middle � limits anterior instability in partially abducted shoulder Inferior � limits anterior instability in ninety abducted shoulder Negative pressure inside shoulder joint. Coracoclavicular screw � screw breakage, cut-out, restricted shoulder actions requiring removal of screw after fracture heals. Plate fixation � supplied the lateral fragment is giant sufficient to take two or three bicortical screws. Newer precontoured locking plates allow for extra screws to be launched in to the lateral fragment. Limited shoulder Management Analgesia and closed reduction in accident and emergency department beneath sedation. Methods of closed reduction for anterior dislocation Hippocrates � traction in line with foot within the axilla 417 Section 7: the trauma oral Stimson � patient is prone with arm hanging over the side with weight attached to the wrist Kocher � shoulder is adducted, externally rotated ( to overcome subscapularis) and then internally rotated In the presence of associated higher tuberosity fracture, there should be a low threshold for performing closed reduction underneath general anaesthesia to forestall fracture propagation to an entire proximal humeral head fracture. There is contradictory proof as to essentially the most appropriate position for shoulder immobilization following closed discount of anterior dislocation, both in a sling with the shoulder internally rotated or in an external rotation brace. The younger the affected person, the higher is the chance for recurrence of shoulder dislocation. Reassess the shoulder after preliminary swelling and pain settle to rule out rotator cuff harm. Associated vascular harm could not current with distal vascular deficit owing to collateral circulation. Any expanding swelling within the shoulder area ought to prompt a vascular consultation and arteriography. Indicators of recurrence: <25 years of age, high-energy injury, large glenoid rim fracture, giant Hill�Sachs lesion and non-compliance with restrictions of shoulder actions. Delayed presentation of posterior shoulder dislocation Closed reduction is usually not potential. Surgical choices for locked posterior shoulder dislocation: Deltopectoral method Disimpaction of humeral head from the posterior glenoid rim by manipulation and or by using a Bankart skid If reverse Hill�Sachs lesion is <50% subscapularis tendon insertion or lesser tuberosity may be transferred to the bony deficit If bony defect is large, then hemiarthroplasty is recommended. Surgical choices for recurrent anterior dislocation Anterior capsulolabral restore (Bankart). If the anterior glenoid defect is >25%, anterior iliac crest block, coracoid switch as anterior block (Latarjet�Bristow), lesser tuberosity switch (Magnuson�Stack). Posterior recurrent dislocation If no bony defects, arthroscopic posterior capsulolabral repair is performed. Open capsulolabral repair for recurrence after surgery and glenoid osteotomy in case of serious glenoid retroversion. Proximal humerus fracture Typical historical past � fall on to shoulder or an outstretched hand Radiological evaluation � variety of fragments, degree of displacement (often difficult or inconceivable to be correct on plain radiographs), angulation and dislocation Initial management � analgesia, polysling. Neer classification is predicated on 4 fragments: humeral head, greater tuberosity, lesser tuberosity and humeral shaft. A combination of these fragments in presence or absence of shoulder dislocation leads to both two-, three- or four-part fracture with or without dislocation. Recurrent shoulder dislocations/instability Two common teams: Traumatic dislocations which would possibly be unidirectional and unilateral. Often require surgical intervention Atraumatic dislocations which are multidirectional and often bilateral. Clinical evaluation � apprehension take a look at, drawer check, Sulcus sign, jerk check for posterior instability. Indications for surgical procedure are associated dislocation, open fracture, neurovascular deficit and displaced fracture. Management If the humeral articular floor is intact (no double shadow indicating a head-splitting fracture), open reduction and locking plate fixation through a deltopectoral approach. In the aged or in these with humeral head-splitting fractures � shoulder hemiarthroplasty is an possibility.
Buy fabramicina without a prescriptionRecurrence could also be seen within the pyelocalyceal systems or ureters antibiotic 932264 buy fabramicina 500 mg mastercard, and customarily current as filling defects or irregular segmental narrowing antibiotics video 100mg fabramicina fast delivery. Anastomotic strictures are usually related to fibrotic strictures virus lokal generic fabramicina 100 mg fast delivery, somewhat than to urothelial tumor recurrence virus ebola sintomas 500mg fabramicina visa. Orthotopic urinary diversions this diversion is the procedure of alternative for many patients, because the urine reservoir is linked to the urethra. The most common technique was described by Studer 32 and is known as the Studer pouch. There is reflux in to both distal ureters (long wwhite arrows), the expected discovering with this form of urinary diversion. There is a filling defect in the left ureteral stump (arrow), which represented recurrence of urothelial most cancers. Strictures on the ureteral ileal anastomosis are most frequently associated to postoperative fibrosis, somewhat than tumor recurrence. Ileal conduit research reveals good opacification of the proper accumulating system and ureter and a standard conduit, but no filling of the left ureter as a result of a stricture on the left ureteral ileal anastomosis. He underwent balloon dilation of the stricture and is now managed with a transconduit drain, which is modified every three months. The pouch-urethral anastomosis has a passable look with no extravasation. Foley catheter was left in place for 2 more weeks, until a repeat study showed resolution of the extravasation (not shown). However, lack of reflux in to the ureters has no significance in a continent diversion, not like an ileal conduit diversion the place absence of reflux is very suggestive of an anastomotic stricture. Next, an ileal phase approximately 50 cm long is chosen, from which an intestinal reservoir is created by completing the following steps. A small opening is created within the distal a half of the pouch, which is then anastomosed to the native urethra. An isoperistaltic afferent limb is created from a 10 cm section of proximal ileum and the ureters are anastomosed to the afferent limb. Bowel continuity is restored by performing a side-to-side or end-to-end ileal anastomosis. The affected person empties the pouch by rising stomach strain and relaxing the pelvic flooring musculature. Contrast infusion is limited to 200 ml, so as to keep away from stressing the brand new anastomotic suture traces. Extravasation might occur from the suture lines in the reservoir, on the ureteral pouch anastomosis, or at the urethral pouch anastomosis. Reflux is often seen in to the ureters if the Studer pouch is crammed to its capacity. Anastomotic strictures could be dilated and stented, however long-term results of ballon dilation are likely to be disappointing in this group of patients. Pouchogram at three weeks after surgical procedure demonstrates a large extravasation on the inferior facet of the anastomosis which was drained percutaneously (long arrow). There is a drainage catheter inside the pouch to promote its healing (short arrows). A segment of the terminal ileum is isolated from the rest of the ileum, and brought to the pores and skin surface as the catheterizing stoma. With present methods, no attempts are made to make the ureteral anastomoses to the pouch nonrefluxing. Diagnosis and administration of colovesical fistulae: six-year experience of ninety consecutive circumstances. Diagnosis of blunt bladder damage: a prospective comparative research of computed tomography cystography and standard retrograde cystography. Experience in a hundred sufferers with an ileal low stress bladder substitute combined with an afferent tubular isoperistaltic phase. Evaluation of the urothelium of the pyelocalyceal systems and ureters is important in patients with a history of hematuria (gross or microscopic), and in sufferers with a historical past of urothelial most cancers. An further indication is evaluation of the residual ureteral stump in a affected person who has undergone a simple nephrectomy for benign illness, or radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma; no ureteral stump is left behind in sufferers with urothelial carcinoma of the higher urinary tract, the place the kidney and the whole ureter are removed together with a cuff of the urinary bladder on the ureteral insertion website.
Cheap 100 mg fabramicina free shippingLocally uti antibiotics have me yeast infection order fabramicina us, the doctor ought to consider for underlying vascular virus bacteria buy fabramicina 100mg with amex, nerve bacteria 2012 buy line fabramicina, tendon bacteria que causa cancer de estomago order cheapest fabramicina, and bone injuries Avulsion sort accidents happen when a flap of tissue is separated from underlying tissue buildings. The most extreme type of this harm is a degloving damage, which occurs when all of the skin and subcutaneous tissues are separated from the underlying fascia. The wound needs pressure irrigation and intravenous antibiotics to scale back the danger of osteomyelitis. Attempts to salvage these limbs are nearly at all times unsuccessful and lead to critical complications and extended hospitalization. Mangled extremity accidents usually contain gentle tissues, neurovascular buildings, and bones. These injuries require a multidisciplinary strategy due to their complexity and high danger of serious problems, including dying, amputation, renal failure, and infection. The native care of large open wounds should be offered in the operating room, typically under common anesthesia. Antibiotic prophylaxis should be administered routinely and tetanus prophylaxis ought to be considered within the applicable cases. Initial priorities ought to embrace hemorrhage control, a fast neurological exam, and pho to documentation. If digital stress is unable to control bleeding a business tourniquet or inflated blood strain cuff could provide temporary hemostasis. Documentation of neurologic perform and extent of tissue harm is necessary in cases where the extremity is unsalvageable and primary amputation needed. Primary repair should be considered only in chosen cases with clear incising wounds. In the majority of cases of in depth soft tissue trauma the wound ought to be debrided and left open to heal by secondary intention. Negative pressure dressings may be useful in removing successfully any infected exudates and forestall the retraction of the wound edges. In extremity injuries the muscle compartments should be monitored clinically and pressure measurements and well timed decompressive fasciotomy ought to be performed in the appropriate cases (see Section 9. Complications the following systemic complications may occur after in depth soft tissue trauma: 1. Hypovolemic shock, due to extravasation of blood and fluid externally or in to the tissues. Electrolytic abnormalities: Hyperkalemia (release of potassium from broken cells), hypocalcemia (deposition of calcium within the injured tissues), or hyperphosphatemia. Compartment pressures should be considered in suspicious extremity injuries to rule out compartment syndrome. Most of these bites happen in children and younger adults and are normally secondary to unintentional provocation or perceived threatening behavior exhibited by the sufferer. Canine bites mostly have an result on the extremities, adopted by the pinnacle and neck, and trunk. However, youngsters usually have a tendency to suffer accidents to the head and neck due to their smaller stature. Injuries on this age group may be devastating as canines can create depressed cranium fractures, massive scalp avulsions, intracranial bleeding, or major vascular injury in the neck or thoracic inlet. Similarly, massive breeds can inflict serious wounds in adults as nicely with bite forces exceeding 450 kilos per sq. inch. Dog bites may cause a selection of harm patterns together with punctures, avulsions, tears, abrasions, and extreme crush damage. Additionally, a excessive diploma of suspicion for occult vascular injury should be maintained in attacks from larger canine breeds or law enforcement animals. Tenets of wound care include initial cleaning and irrigation which serves to take away particles and micro organism, and has been proven to decrease the transmission of the rabies virus. For giant wounds, x-rays are essential to rule out retained international our bodies and underlying fractures. Liberal session of an orthopedic specialist ought to be obtained when the chunk entails the hand. The hand accommodates a number of bones, nerves, and joints enclosed inside a small house and comparatively superficial location.
Fabramicina 250mg lineNote: Consult package insert for detailed directions on reconstitution of streptokinase previous to virus maker fabramicina 500mg with mastercard administration virus nyc buy discount fabramicina 500 mg on line. Reteplase (Retavase) Indication Acute myocardial infarction Dosage Adults Treatment should be initiated as quickly as attainable antibiotic list for uti 100 mg fabramicina mastercard, ideally inside 12 h after the onset of chest pain antibiotic heartburn fabramicina 100 mg otc. Reteplase ought to be administered as two 10-unit bolus injections each administered over 2 min, the second dose given 30 min after the initiation of the primary injection. Note: Reteplase ought to be given via an intravenous line by which no different medicines (eg, heparin) are being injected or infused. If reteplase is to be administered by way of an intravenous line containing heparin, the road ought to be flushed earlier than and after reteplase administration with both zero. Reteplase should be reconstituted with 10 mL of sterile water for injection (without preservatives) to yield an answer of 1 U/mL. The vial must be swirled gently to dissolve the drug, taking precaution to keep away from shaking. Once dissolved, 10 mL should be withdrawn from the vial in to a syringe for administration to the patient. Angina Initiate with forty mg as soon as daily; dosage could additionally be elevated by 40-80 mg/d each 3-7 days till sufficient management of angina is achieved. Note: Because of the lengthy half-life of nadolol, oncedaily dosing is enough to present stable plasma concentrations. Adjustments in dosing intervals should be made for sufferers with renal impairment as follows: CrCl (mL/min/1. Preparations Corgard (Monarch): 20, 40, eighty, 120, one hundred sixty mg tablets Fixed-Dose Combinations for Treatment of Hypertension: Corizide 40/5 tablets-40 mg nadolol and 5 mg bendroflumethiazide Corizide 80/5 tablets-80 mg nadolol and 5 mg bendroflumethiazide *This is the volume of tenecteplase to be administered as a single bolus dose over 5 s after one vial of tenecteplase (50 mg) is reconstituted with 10 mL of sterile water for injection. Nadolol (nadolol, Corgard) Indications Angina Hypertension Dosage Adults Hypertension Initiate with 20-40 mg once daily; dosage may be increased steadily in increments of 40-80 mg to a maxi- 680 Appendix2 wanted as a lot as a maximum of 320 mg/d. Cardiac arrhythmias Regular formulation: 10-30 mg three to 4 instances per day given earlier than meals and at bedtime. Essential tremor Regular formulation: Initiate with 40 mg twice daily; dosage may be titrated according to response to a maximum of 320 mg/d. Hypertension Regular formulation: Initiate with 40 mg twice daily; dosage may be increased gradually in accordance with response to a maximum of 640 mg/d. Extended-release formulation: Initiate with eighty mg as soon as daily; dosage may be elevated gradually according to response to a most of 640 mg/d. Hypertrophic subaortic stenosis Regular formulation: the usual dose range is 20-40 mg three to four times per day given before meals and at bedtime. Myocardial infarction Regular formulation: the standard dose range is 180-240 mg/d given in three to 4 divided doses. Migraine prophylaxis Regular formulation: Initiate with 80 mg/d in divided doses; dosage could additionally be elevated gradually to the standard range of 160-240 mg/d in divided doses. Pheochromocytoma (adjunct remedy to a-adrenergic blocker): Regular formulation: 60 mg/d in divided doses for three days previous to surgical procedure. To prevent extreme hypertension caused by unopposed a-adrenergic stimulation, treatment with an a-adrenergic blocking agent should always be began prior to the usage of propranolol and continued throughout propranolol therapy. As an adjunct to prolonged remedy of inoperable pheochromocytoma, 30 mg of propranolol every day in divided doses together with an a-adrenergic blocker is normally sufficient. Intravenous administration for life-threatening arrhythmias the identical old dose is 1-3 mg given under careful monitoring. Dosage may be increased at 3- to 5-day intervals to traditional vary of 2-4 mg/kg/d given in divided doses. The dose should be adjusted based on clinical response to a maximum of 30 mg/d given in divided doses. Preparations Timolol (generic); Blocadren (Merck): 5, 10, 20 mg tablets Timolol (generic): zero. Myocardial infarction Treatment should be initiated with intravenous atenolol 5 mg administered over 5 min, followed by a second intravenous dose of 5 mg 10 min later. If the patient tolerates the complete intravenous remedy, 50 mg of atenolol ought to be administered orally 10 min after the final intravenous dose, followed by a second 50 mg oral dose 12 h later. Then the affected person can receive atenolol orally either one hundred mg as soon as daily or 50 mg twice every day for 6-9 days or till discharge from the hospital. Note: Because atenolol is eliminated mainly within the kidneys as unchanged drug, dosage adjustment should be made in sufferers with renal impairment.
|



