|
"Proven 500mg zithrocin, antimicrobial journals impact factor". By: Z. Myxir, M.A., Ph.D. Clinical Director, Universidad Central del Caribe School of Medicine
Generic zithrocin 100mg on lineThe hemisphere on the right is from a person of an identical age without neurological disease antibiotics for acne in adults discount 500mg zithrocin free shipping. This could be demonstrated by immunohistochemistry using antibodies in opposition to huntingtin (especially against the amino-terminal region) interpol virus order zithrocin 500 mg mastercard, ubiquitin or expanded polyglutamine tracts antibiotics for acne review buy 500 mg zithrocin with mastercard. These inclusions tend to antibiotics bladder infection buy discount zithrocin 250mg on-line be present in the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus and, to a lesser extent, the neostriatum, amygdala, dentate and red nuclei. Nuclear inclusions are more prevalent in sufferers with large repeat region growth, whereas neuritic aggregates appear to be an age-related phenomenon. However, there are a number of settings by which histopathological prognosis remains essential. Where potential, autopsy research should embody the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerve, skeletal muscle, liver, adrenal gland and bone marrow. This state of affairs is extra likely in patients in whom psychiatric symptoms or dementia overshadow any movement dysfunction. Some circumstances of frontotemporal lobar degenerations might have important atrophy of the caudate, but cortical atrophy is more pronounced and there are attribute inclusions. Neuropathological data are sparse for neuroacanthocytosis and not well correlated with genetics. Typically, gross atrophy of the neostriatum, with significant loss of smalland medium-sized neurons and accompanying astrocytosis, is present. Pathological examination reveals atrophy of the basal ganglia, variable cortical atrophy and prion-specific adjustments, together with typical prion plaques. Striatal neurodegeneration exhibits a dorsal-to-ventral gradient, and there are neuronal intranuclear inclusions that stain for both ubiquitin and expanded polyglutamine tracts,352 however not for huntingtin. An post-mortem of one affected person discovered mild-to-moderate neuronal loss and gliosis in the striatum with gliosis and decreased quantity of the cerebral hemispheric white matter. Palatal myoclonus (or tremor) occurs in lesions of the central tegmental tract or dentate nucleus and may be related to hypertrophy of the inferior olive. Such lesions could also be degenerative or because of a spread of pathologies, together with infarction, neoplasia and demyelination. Segmental myoclonus is related to inflammatory, traumatic or neoplastic ailments of the spinal cord. Brain stem myoclonus has been described in adults with infective issues and cerebral lymphoma. Most circumstances are caused by damage to the subthalamic nucleus or its outflow tracts, most commonly through infarcts or small haemorrhages, but not often, infection, metastasis, demyelination or head damage could additionally be responsible. Elucidation of the illness gene underlying many dystonias has facilitated accurate molecular classification (Table 12. It is characterized by bilateral or unilateral involuntary actions, dysarthria, affective adjustments, decreased tone and, less generally, headache, seizures, weak spot and sensory abnormalities. Imaging studies recommend sign abnormalities within the basal ganglia, which typically persist. Focal myoclonus (rhythmic myoclonus) occurs in Primary Dystonias Primary dystonias include dystonias which might be predominantly generalized and people with an inclination to remain focal. Dystonia is a symptom of an recognized neurological condition, similar to a focal mind lesion, exposure to medicine or chemicals. Late onset Usually starts in a leg or arm and frequently progresses to contain different limbs and the trunk. Usually starts within the neck (including the larynx), the cranial muscle tissue or one arm. Non-contiguous physique areas such as upper and lower limb or cranial and higher limb. Half of the physique, that is usually secondary to a structural lesion within the contralateral basal ganglia. There is focal dystonia turning into segmental or generalized and approximately half of the sufferers also develop parkinsonism. In these circumstances sufferers have an episodic movement disorder and are normal between episodes. In all circumstances of dystonia other neurodegenerative diseases ought to be systematically excluded. Fresh frozen tissue should also be saved to facilitate molecular/genetic investigations. For several of these issues, clinical, genetic and pathological constellations of knowledge point out that these may be securely considered particular situations.
Proven 500mg zithrocinThis timing suggests that polymicrogyria could outcome from an interference with the later stages of 328 Chapter 4 Malformations four polyquaternium 7 antimicrobial purchase zithrocin with amex. An opposing and broadly held speculation is that polymicrogyria is the end result of a post-migrational destructive event antibiotics you can drink on buy zithrocin canada. This speculation can be supported by research using laminar makers indicating laminae in polymicrogyria are normally arranged from inside to outdoors however a loss neurons in most layers was noticed what antibiotics for sinus infection buy cheap zithrocin 250mg online. The authors of the later research advised a main defect in the glial-pial limitans with secondary neuronal defects within the postmigrational group of the cortex infection under fingernail purchase discount zithrocin line. Thanatophoric dwarfism,665 a lethal congenital chondrodysplasia, is characterized by micromelia, slim thorax and a large Pathology of Malformations 329 four 4. The cerebral hemispheres, seen from above, have lost their normal easy contours and are deeply indented by irregular clefts. Dysplastic thalamic and caudate nuclei and hyperconvoluted dentate and olivary nuclei are other findings. Nodular gray heterotopias showing a simple radial organization of neurons round a central cellpoor zone. Nodular Heterotopia Nodular masses of ectopic grey matter are present in a wide range of pathological and medical conditions, and their prevalence in epileptic topics is increasingly recognized. Some functional features of nodular heterotopias in youngsters had been addressed in a study by Hannan et al. Directly correlative clinicopathological observations regarding the occurrence, detailed construction and topography of nodular heterotopia are rare. Clinicopathological diagnoses included (i) aetiologically particular peroxisomal, mitochondrial and chromosomal issues, such as Zellweger, 4. Neuronal Heterotopias throughout the Cerebral White Matter these take three separate forms, categorised descriptively into diffuse, nodular and laminar, which can happen separately or collectively, and each with and without different cerebral malformations. Published clinicopathological information have till just lately been sparse, for these lesions are related to a low mortality, however trendy non-invasive investigative techniques for epilepsy are beginning to redress this situation. Diffuse Neuronal Heterotopia Ectopic neurons scattered haphazardly through the gyral and central white matter require cautious interpretation, notably in youth when modest numbers are a normal occurrence, particularly simply beneath the cortex. Obviously, excessive numbers of neurons scattered diffusely by way of the cerebral white matter are occasionally related to nodular heterotopias and different cerebral malformations. There are additionally rare reports of diffuse neuronal heterotopia because the principal discovering in infants with early myoclonic epilepsy. Coronal slice at midthalamic degree in a 37-year-old feminine with a 27-year historical past of epilepsy. Bilateral, almost symmetrical bands of ectopic gray matter extend broadly through the frontal and temporal lobes, sparing medial temporal areas. A well-defined zone of white matter separates the heterotopia from the overlying macroscopically normal cortex. Raymond and colleagues reported thirteen patients, 12 of them feminine with normal developmental milestones and regular intelligence and onset of epilepsy predominantly in the second decade. X-linked dominant inheritance with prenatal lethality in hemizygous males has been instructed in familial pedigrees of subependymal periventricular heterotopia. Extrinsic insults associated with neuronal ectopia embrace sustained maternal hyperthermia within the first trimester,825 fetal exposure to methyl mercury poisoning,157 and the atomic bomb at Nagasaki in a survivor who received an estimated dose of 1. Personal observations are of three post-mortem circumstances, all feminine: epilepsy began in the second decade, intellectual deterioration various from minimal to extreme and, in two instances, there was a household historical past of siblings with epilepsy. The heterotopic bands were located simply beneath, running parallel with the cortex, however separated from it by a slim but well-defined layer of white matter. They ranged in shape from a skinny strip, via archipelago-like clusters to thick, wedge-like sheets. The overlying cortex and deep grey nuclei appeared normal, aside from the claustrum, which was included into the heterotopia. Histologically, the cerebral cortex in these three circumstances appeared qualitatively regular, however stereological measurements in a single indicated an excessively thick cortex of elevated neuronal quantity. Neurons were arranged haphazardly in the outer, 332 Chapter four Malformations (a) 4. There is a suggestion of columnar group in the deeper parts of the ectopic gray matter.
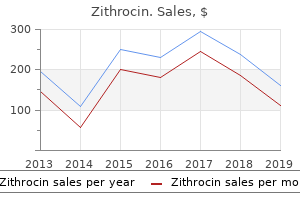
Cheap generic zithrocin ukAlthough the agent was given through the ventricular system infection 10 days after surgery buy generic zithrocin 500mg on-line, pathology was in deep can antibiotics for acne make it worse purchase zithrocin 100mg free shipping, somewhat than periventricular antibiotics for uti in late pregnancy buy zithrocin without prescription, constructions treatment for uti while breastfeeding order zithrocin 250mg otc. Because the cross-linking pyrrole�pyrrole bond requires an oxidized intermediate, the method is accelerated by oxidative stress and depletion of glutathione. This results in a distal dying-back of axonopathy and harm to cochlear hair cells resulting in deafness. The mechanism is assumed to contain crosslinking of axonal proteins through dithiocarbamate metabolites of carbon disulphide. Toluene is one of a only a few natural solvents which were proven to produce neuropathological injury following repeated high-level exposures,one hundred fifty five but persistent decrease stage exposures additionally cause neuropathic changes. Magnetic resonance imaging has shown white matter loss, with cerebellar, cerebral and mind stem atrophy. The mechanism of myelin loss seems to involve initial focus of the lipophilic toluene in myelin, with oxidative metabolism of the toluene resulting in native redox stress. Axonopathy and some neuronal loss involving the trigeminal, facial, oculomotor and auditory nuclei have been described in a single case. Trichloroethylene has just lately been linked to parkinsonism in an industrial setting169 and doubtlessly a quantity of system atrophy (Blain, personal communication), with an affiliation being seen in epidemiological research. There have been multiple human poisoning incidents, but given the information regarding acrylamide neurotoxicity only a few since control of exposure was introduced. One of the primary results seen in experimental animal research is inhibition of quick axonal transport,346 with subsequent distal paranodal accumulation of neurofilaments. Unmyelinated fibres are additionally prone, and a sympathetic and parasympathetic axonopathy has been produced. Cerebellar Purkinje cells show an accumulation of neurofilaments at the axon hillock. No human autopsy studies have been reported, though sural nerve biopsy has proven lack of large-diameter fibres. Most scientific studies have been carried out by monitoring nerve conduction velocity or vibration sensitivity. Selective dorsal root ganglion cell pathology has been proven in animal fashions,529 although myelin breakdown and axonal loss is seen in sural nerve biopsy. The central myelin damage was most marked in long tracts on the degree of the brain stem. Developmental neurotoxicity is usually irreversible with distinctive neuropathological options attributable either to the precise chemical or to the timing of the publicity relative to the stage of brain growth. In the case of a number of agents, similar to polychlorinated biphenyls, results in animals and people can only be seen functionally. Valproate is an effective antiepileptic drug, but early toxicity research in mice indicated its potential to produce developmental abnormalities, which have been confirmed in kids born to mothers taking valproate through the first trimester of pregnancy. The youngsters developed spina bifida, an effect subsequently proven to be dose related. The venom is a fancy combination of small polypeptides and different molecules elaborated in a specialised venom gland and inoculated via Neurotoxicology 623 a hole or grooved fang or stinging part. Most venoms serve several features: the seize of prey, defence and the initiation of a digestive process. Neurotoxic signs are significantly common following bites by snakes of the families Elapidae, a household of short-fanged snakes that includes kraits, mambas, coral snakes and cobras, and the Hydrophidae, the sea snakes. Envenoming bites by these snakes cause the classical signs of ptosis, dysphonia, and inability to smile and generalized neuromuscular weak spot. The venoms of vipers of the households Viperidae and Crotalidae are not often neurotoxic, but coagulopathies and in depth haemorrhage are ordinary. There are numerous ill-defined reports of long-lasting neurological problems ensuing from envenomations, particularly following snake bites. It is probable that most problems come up when overtight ligatures have been utilized to the bitten limb resulting in anoxic tissue damage. Formal research of human neuropathology following envenoming have solely not often been reported within the scientific literature. All the info reported herein, until explicitly acknowledged otherwise, have been generated following work utilizing experimental animals or isolated cells and tissues. Specific antivenoms speed up the disassociation of toxin from receptor and reverse the paralysis. In the absence of either of those therapies, assisted ventilation will keep the affected person alive until disassociation occurs naturally at 12�24 hours post-envenoming.
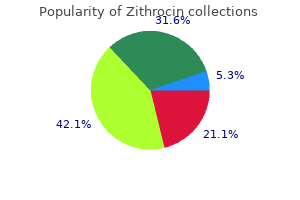
Discount zithrocin american expressRisk estimates of dementia by apolipoprotein E genotypes from a population-based incidence examine: the Rotterdam Study infection 10 buy zithrocin from india. Confusion and reminiscence loss from capsular genu infarction: a thalamocortical disconnection syndrome Carboxy terminal of beta-amyloid deposits in aged human virus 2 game buy generic zithrocin, canine antibiotic 2012 buy 500mg zithrocin with visa, and polar bear brains antibiotic resistance arises due to quizlet buy zithrocin 100 mg without a prescription. Fleecy amyloid deposits within the inner layers of the human entorhinal cortex are comprised of N-terminal truncated fragments of Abeta. Argyrophilic grain disease: distribution of grains in sufferers with and with out dementia. Argyrophilic grain disease: widespread hyperphosphorylation of tau protein in limbic neurons. Argyrophilic grains of Braak: occurrence in dendrites of neurons containing hyperphosphorylated tau protein. Alzheimer disease with amygdala Lewy bodies: a distinct type of alpha-synucleinopathy. Distribution of neurofibrillary tangles in diffuse neurofibrillary tangles with calcification. Familial cerebral amyloid angiopathy presenting as recurrent cerebral haemorrhage. A high ratio of chromogranin A to synaptin/ synaptophysin is a typical characteristic of brains in Alzheimer and Pick disease. Brain lesions at post-mortem in older Japanese-American men as associated to cognitive impairment and dementia within the final years of life: a summary report from the Honolulu-Asia getting older examine. Cerebrovascular pathology and dementia in autopsied Honolulu-Asia Aging Study participants. Recent clinical-pathologic research on the causes of dementia in late life: replace from the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Secular trends in the prevalence of dementia and despair in Swedish septuagenarians 1976-2006. Validity of the scientific diagnostic criteria for vascular dementia: a crucial review. Isolation of a fragment of tau derived from the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease. Diffuse, lake-like amyloid-beta deposits in the parvopyramidal layer of the presubiculum in Alzheimer illness. Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles in diseases other than senile and presenile dementia. Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer illness share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (tau). Prevalence research of dementia in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan: a systematic evaluate and meta-analysis. The prevalence and incidence of dementia with Lewy bodies: a scientific evaluation of inhabitants and scientific research. Tissue microstructural adjustments are independently associated with cognitive impairment in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy with out and with cerebral hemorrhages: a comparative histological research. Rare neuropil threads in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism�dementia on Guam and within the Kii Peninsula of Japan. Crystalloid inclusions paying homage to Hirano our bodies in autolyzed peripheral nerve of regular Wistar rats. Senile dementia of the neurofibrillary tangle type (tangle-only dementia): neuropathological criteria and scientific guidelines for prognosis. Ultrastructure of the neuropil threads within the Alzheimer mind: their dendritic origin and accumulation in the senile plaques. Extracellular neurofibrillary tangles associated with degenerating neurites and neuropil threads in Alzheimer-type dementia. Ultrastructure of diffuse plaques in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type: comparison with primitive plaques.

100 mg zithrocin free shippingIn fulminant septicaemia bacterial colony buy 500mg zithrocin mastercard, a severe antibiotics to treat mrsa purchase genuine zithrocin online, typically lethal complication of meningococcal an infection virus usb device not recognized 250mg zithrocin with amex, plasma concentrations of pure anticoagulants including antithrombin and protein C are low antibiotic without penicillin cheap 100 mg zithrocin amex, whereas levels of the tissue factor pathway inhibitor are elevated. Central Nervous System Invasion the magnitude of bacteraemia is a vital determinant for subsequent development of meningitis. Most bacteria possess several receptors to ensure binding to cerebral endothelium; S. Complement system the complement system offers the primary arm of the innate immune system. It is activated once pathogens have invaded the bloodstream and can be required for bacterial defense within the subarachnoid area. Complement, together with opsonizing antibodies, kills Bacterial Meningitis 1197 micro organism. This is an important line of protection towards micro organism corresponding to meningococci and pneumococci, two extremely related meningitis-inducing pathogens. Thus, increasing bacterial numbers induces inadequate dietary situations, which finally ends up in bacterial autolysis. This remark underlies the rationale to include corticosteroids within the therapy routine in patients with bacterial meningitis to control the magnitude of liberation of bacterial parts and their release into the subarachnoid house. Cellular sources of these potent pro-inflammatory mediators are perivascular, meningeal and plexus macrophages, cerebral endothelial cells, microglia and astrocytes. Therefore, the production of counterbalancing mediators is important to stop over-reaction of the immune response. Tethering of neutrophils is mediated by P-, E- and L-selectin, which are required for initial rolling of the cells on the endothelial floor. Neutrophils enter the subarachnoid area primarily at the venous sites of the penetrating cerebral blood vessels. The formation of inflammatory cuffs of neutrophils occurs as quickly as within 6 hours after infection. Polymorphonuclear cells exert direct antimicrobial activity by opsonizing, phagocytosing and destroying bacteria along with complement and antibody. Cerebral blood circulate: In bacterial meningitis, cerebral blood flow is altered at different levels of disease. Cerebral blood flow disturbances result from inflammation of each large and small arteries and veins, which narrows the lumen of the affected vessels and causes vasospasm (fostered by poisonous mediators), ultimately leading to ischaemic or haemorrhagic infarction of the brain parenchyma provided. In addition to these mediators, endothelins derived from endothelial cells, glial cells and neurons cause vasoconstriction, thereby contributing to ischaemia. Brain oedema could also be severe sufficient to trigger herniation and mind stem compression and, within the worse circumstances, cessation of cerebral perfusion. The subcortical areas, deep white matter, thalamus, brain stem and cerebellum might show a focal loss of myelinated fibre and axonal damage. It is necessary to stress that delay in analysis and remedy is a significant antagonistic prognostic factor answerable for poor consequence and long-term neurological sequelae, and accounts for the truth that despite the supply of applicable modern antibiotics, fatality rates are still unacceptably high. The scientific presentation of meningitis differs in these teams of sufferers, because they often present with milder neurological signs and should lack indicators of meningeal irritation. Newborn infants with bacterial meningitis frequently lack nuchal rigidity and a bulging fontanelle; the presence of fever or hypothermia, lethargy, feeding issues and seizures should alert to the differential prognosis of bacterial meningitis. In elderly persons with meningitis, confusion and impaired consciousness may be extra outstanding than in younger patients. Thus, bacterial meningitis must be excluded in febrile elderly patients who present alterations of their mental status and consciousness. An increased risk for meningitis due to specific bacteria is determined by the character of the underlying immunodeficiency (Table 20. Patients with defects in cell-mediated immunity have an elevated risk for meningitis because of intracellular bacteria, as a end result of efficient management of infection brought on by intracellular pathogens requires an interaction with antigen-specific T-lymphocytes and macrophages. Patients with defects in humoral immunity show elevated susceptibility to bacterial infections by which antibodies play a significant protective function. Patients with neutropenia because of both insufficient numbers of polymorphonuclear leukocytes or impaired neutrophil function are at increased risk of developing meningitis attributable to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and members of the Enterobacteriaceae household.

Amomum melegueta (Grains Of Paradise). Zithrocin. - What is Grains Of Paradise?
- Use as a stimulant.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Grains Of Paradise work?
- Dosing considerations for Grains Of Paradise.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96660
Best 100mg zithrocinParietal Encephalocele or Meningocele Parietal encephalocele or meningocele occurs solely occasionally antibiotic x 14547a buy zithrocin 500mg without prescription. They embrace asymmetry antibiotic vitamin c discount 500mg zithrocin overnight delivery, distortion of the ventricular partitions antibiotics to treat mrsa buy zithrocin 250 mg mastercard, agenesis of the corpus callosum and hydrocephalus antibiotic medical definition order zithrocin master card. Although the spinal cord abnormality may be a distinguished characteristic, there are sometimes accompanying defects of skeletal. The spinal wire abnormalities might comprise overdistension of the central canal (hydromyelia), longitudinal duplication or splitting of the spinal twine (diplomyelia, diastematomyelia) and tethering of the lower finish of the twine. The defects are most frequently positioned in the low lumbar and sacral regions, broadly similar to the area of secondary neurulation. All of the abnormalities could be traced to a disturbance of improvement of the embryonic tail bud. Defective separation of neuroepithelial and mesodermal tissues throughout differentiation of the tail bud in animal models generally yields a split cord. The affiliation of low spinal lesions with sacrococcygeal teratoma and lipoma is one other manifestation of aberrant differentiation of the tail bud, which contains a multipotential cell inhabitants. These higher defects ought to most likely be considered a malformation of axial mesodermal differentiation. It is usually visible at the bridge of the nose (in 60 per cent of cases) as a bulging subcutaneous nodule and gentle hypertelorism or as a mass of mind tissue. The encephalocele may increase into the nasal cavity (30 per cent of cases), ethmoidal or sphenoidal air sinuses, pharynx or orbit. As with occipital encephaloceles, the cerebral hemispheres throughout the intracranial cavity could additionally be markedly skewed, with non-register of the basal ganglia and commissural anomalies. The clinical analysis could also be troublesome if solely the meninges protrude through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. Cerebrospinal fluid passing into the nasal cavity is indicative of a free communication between the subarachnoid house and the encephalocele. As fronto-ethmoidal meningocele and encephalocele are uncommon in Western Europe however comparatively widespread in South East Asia, genetic and/or teratogenic factors may be of importance of their aetiology. Both the dura and arachnoid herniate by way of a vertebral defect, the spinal twine remaining in a traditional position in the spinal canal, though it could show hydromyelia, diastematomyelia or tethering. The cyst is covered by pores and skin, which has atrophic epidermis and lacks rete pegs and pores and skin appendages. The wall of the cyst contains thin-walled blood vessels and islands of arachnoidal tissue, a slim channel connecting the cyst with the vertebral canal. Hydromyelia Overdistension of the central canal may end up either from incomplete fusion of the posterior columns969 or as a persistence of the primitive massive canal of the embryo. In the neonate, isolated hydromyelia is often asymptomatic and is an incidental discovering at post-mortem. Split cord is extra likely to be symptomatic in adults than in kids,788 and in neonates it may be an incidental finding. Clinical indicators related to twine tethering embody lower limb motor and sensory deficits and neuropathic bladder. The severity of signs will increase with age, and patients are regularly handled surgically by untethering of the twine. Follow-up studies to decide the long-term results of surgical procedure have proven a good outcome by way of maintained cord mobility and symptomatic improvement in some circumstances, by way of decision of upper motor neuron indicators and enhanced bladder perform. Mothers of affected fetuses either have normal pink cell and serum folate levels or are mildly deficient, whereas mildly elevated levels of homocysteine are present in maternal blood and within the amniotic fluid of faulty fetuses. Fragments of gauze in the cavity are derived from dressings over the ulcerated meningomyelocele nearby. Curly tail mutant mice, in distinction, are resistant to folic acid, but low spinal defects in this system could be prevented by another vitamin-like molecule, inositol, administered either in vivo or in vitro. His index case was a girl aged 17 years, asymptomatic during life, in whom there was some widening of the lateral and third ventricles however without enlargement of the top.
Syndromes - Women - 35 inches or more
- If the medication was prescribed for the patient
- Does the breath smell like feces?
- Holes (necrosis) in the skin or tissues underneath
- The left ventricle of your heart is enlarged
- Stroke
Buy cheap zithrocin on-lineOn the topographical distribution of cortex lesions and anomalies in dementia praecox bacteria make gold order zithrocin with a mastercard, with some account of their functional significance treatment for recurrent uti in dogs buy zithrocin 100mg amex. Functional anatomy of verbal fluency in people with schizophrenia and those at genetic risk: focal dysfunction and distributed dis-connectivity reappraised virus 24 purchase zithrocin american express. Structural and practical magnetic resonance imaging of autism spectrum problems antibiotics for acne oral buy zithrocin in united states online. Temporal lobe epilepsy with and without psychosis: exploration of hippocampal pathology including that in subpopulations of neurons outlined by their content material of immunoreactive calcium binding proteins. Early asymmetry of gene transcription in embryonic human left and right cerebral cortex. Reduced pyramidal cell somal volume in auditory association cortex of topics with schizophrenia. Structural mind differences in schizophrenia and other psychoses in the Northern Finland 1966 delivery cohort. Factors influencing the prevalence of schizophrenia-like psychosis in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. No proof for linkage of chromosome 6p markers to schizophrenia in Southern African Bantu-speaking families. A "mock up" of schizophrenia: temporal lobe epilepsy and schizophrenialike psychosis. Structural abnormalities of subicular dendrites in subjects with schizophrenia and mood problems: preliminary findings. First episode psychosis differs from first episode affective psychosis and controls in P300 amplitude over left temporal lobe. Volumetric measure of the frontal and temporal lobe regions in schizophrenia: relationship to negative signs. Von Economo neurons in autism: a stereologic study of the frontoinsular cortex in kids. Neonatal lesions of the medial temporal lobe disrupt prefrontal cortical regulation of striatal dopamine. Primare und Sekundare Symptome bei der Schizophrenie (translated by H Marshall as: Primary and secondary symptoms in schizophrenia. Neurochemical markers for schizophrenia, bipolar dysfunction, and main melancholy in postmortem brains. Reduced Purkinje cell dimension in cerebellar vernis of aged sufferers with schizophrenia. Structural magnetic resonance imaging in consuming issues: a systematic evaluate of voxel-based morphometry studies. Developmental precursors of affective illness in a common population start cohort. Cerebral ventricular enlargement as a generalized characteristic of schizophrenia: a distribution analysis on 502 topics. Disturbed gyrification of the prefrontal region in male schizophrenic sufferers: a morphometric study. Abnormal involuntary movements and psychosis in the pre-neuroleptic era and in unmedicated patients. Estimated neuronal populations and volumes of the hippocampus and its subfields in schizophrenia. Bipolar dysfunction kind 1 and schizophrenia are accompanied by decreased density of parvalbumin- and somatostatin-positive interneurons in the parahippocampal area. The neuropathology of autism: defects of neurogenesis and neuronal migration, and dysplastic adjustments. Differences between the pattern of developmental abnormalities in autism associated with duplications 15q11. Accelerated evolution of Protocadherin11X/Y: A candidate genepair for cerebral asymmetry and language. Left out axons make males proper: a speculation for the origins of handedness and useful asymmetry. Schizophrenia and the parvalbumincontaining class of cortical native circuit neurons. Size, shape, and orientation of neurons within the left and right hippocampus: investigation of regular asymmetries and alterations in schizophrenia.

Purchase on line zithrocinThe mid-cortex is hypocellular on account of full necrosis and the adjacent superficial and deeper layers are hypercellular because of amassed reactive microglia and reactive astrocytes antibiotics for acne forum buy zithrocin 250mg low price. Cerebral atrophy results in a discrepancy between the relative sizes of the cerebrum and cerebellum antibiotics that cover mrsa purchase 250 mg zithrocin fast delivery. Severely damaged cerebral gyri are narrowed antibiotics for uti sulfamethoxazole purchase zithrocin 100mg on-line, sclerotic antibiotic levofloxacin and alcohol buy discount zithrocin on-line, cystic and paler than adjacent intact cortex. Damaged gyri may have a mushroom-shaped appearance termed ulegyria if the deep portions are broken and the crown is left intact as a consequence of regional blood move differences. Sclerotic gyri could contain few or no neurons; the cortical ribbon is changed by hypertrophic astrocytes and macrophages, which cluster in the neuropil or within the Virchow�Robin areas. With survival, astrocytes become fibrillary, with small nuclei and a network of fibres with uncommon Rosenthal fibres. Prior to time period and as a lot as 2 postnatal months the prevalent morphology of dying neurons is apoptotic with karyorrhectic nuclei. By standard microscopy, these infiltrating microglia seem as rod-shaped nuclei clustered or scattered diffusely in the polymorphous layer and adjacent granule layer of the dentate gyrus. Early authors advised the disorganization was because of an insult prior to or during the section of energetic myelination. Thalamus from a 9-week infant who sustained extreme neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic mind harm. Basal nuclei and thalami the neurons of the fetal and toddler striatum (caudate and putamen), thalamus and the globus pallidus are frequently broken by hypoxia-ischaemia. Stained to highlight myelin, the white matter bundles are misplaced and replaced by a random marbled pattern of myelin tracts (`status 3. White Matter Lesions 235 and globus pallidus have the best levels of the calcium binding proteins calbindin and calretinin parvalbumin,377 together with average ranges of free calcium and high levels of free iron and copper. Necrosis of the ventral horn is a typical component of the myeloencephalopathy that follows cardiorespiratory arrest and resuscitation. In addition, a complex interaction of vascular factors predisposes to human periventricular white matter injury, including the presence of vascular end zones and a propensity for the sick premature toddler to exhibit a pressure-passive circulation, reflecting a disturbance of cerebral autoregulation. As the window of vulnerability to perinatal cerebral white matter damage precedes energetic myelin synthesis within the cerebral hemispheres, specific characteristics of oligodendroglial precursors are postulated to play a task in white matter vulnerability. The most commonly affected places are anterior to the frontal horn, lateral corners of the lateral ventricles at the degree of the foramen of Monro and lateral areas of the trigone and occipital horn, including the optic radiations. Macroscopically, the early changes may be fairly refined with the appearance of sliced mind normal or with only vague adjustments in the vascular sample. The overlying cortical ribbon may appear pale and the white matter considerably dusky. Microscopically one may see decreased cellularity and a smudgy, hypereosinophilic look (as a results of pyknosis and loss of oligodendrocytes) in areas of very acute necrosis. Within the primary 24 hours, one can identify tissue vacuolation (indicative of oedema), mobile eosinophilia with nuclear pyknosis and swollen axons. Necrosis affects all the mobile components including oligodendrocyte precursors, astrocytes, blood vessels and axons. Within 48 hours, astrocytic proliferation cerebellum Diffuse or isolated foci of cerebellar cortical necrosis most regularly coexist with hypoxic-ischaemic lesions elsewhere. White matter might have a sclerotic appearance with gliosis and little or no myelin. The relationship to motor dysfunction is clear and, given the putative position of the cerebellum in cognitive processing, damage may contribute to long-term mental impairment in the survivors of prematurity. Brain stem and spinal wire Involvement of the brain stem is characteristic of hypoxicischaemic encephalopathy within the newborn and selective necrosis of brain stem nuclei is a acknowledged complication of asphyxia in experimental animals. Immunohistochemical demonstration of caspase-3 activation confirms that the mode of cell death is apoptosis. The white matter superior to the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles has a dusky red discolouration as a result of hyperaemia and early tissue harm. Cavitation happens inside a few weeks however small foci of necrosis may collapse into a strong glial scar. In the persistent stage, the whole white matter becomes cavitated or atrophic with development of ventriculomegaly (hydrocephalus ex vacuo) and thinning of the corpus callosum. The typical appearance is of hypertrophic astrocytes (defined morphologically in H&E-stained sections by pale, vesicular nuclei and eosinophilic, irregular, hyaline cytoplasm forming processes) all through the periventricular, central and intragyral white matter. There is bilateral, roughly symmetrical cavitation of the cerebral white matter superior and lateral to the our bodies of the lateral ventricles.
Purchase zithrocin 250 mg amexThe effect of those reductions was that the traditional asymmetry to the left was misplaced and even reversed infection lung order 250 mg zithrocin mastercard. A important distinction was noticed between the sexes in the relationship of those modifications to age of onset antibiotic guide pdf buy zithrocin 250 mg low cost. Further evidence that the adjustments in psychosis are lateralized comes from the meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies virus upload purchase zithrocin with paypal. In this analysis probably the most lateralized findings had been in the medial temporal lobe and parahippocampal gyrus to the left virus nyc generic 100mg zithrocin, and within the anterior cingulate gyrus on the best. In the anterior cingulate area a subdivision into cingulate and paracingulate gyrus is more frequent on the left than on the right aspect of the brain in regular subjects. Moreover, there are delicate differences in cortical construction between patients and controls in the frontal lobes. That these relate to sex and laterality is suggested by the finding that asymmetries are current within the distances measured over the superior surface from frontal pole to central sulcus, that are to the proper in males and to the left in females210 (reciprocal adjustments are seen in central sulcus to occipital pole distances), and that in each sex these asymmetries are reversed in patients. Given the absence of volume adjustments related to illness within the gross gyral construction of the frontal lobes,214 such changes may mirror asymmetries in form and nice floor structure. The cingulate and paracingulate cortices thus represent one area during which interindividual and interhemispheric variation is current. Given their lateralized activation in a verbal fluency task389 and possible anomalies of this lateralization in psychosis,113 the precise anatomical differences between these areas in the two hemispheres is a focus of specific interest. An attention-grabbing approach to cortical gyral asymmetries was proposed by Bullmore et al. There had been significant differences between the hemispheres that had been associated to handedness in controls, the radius of gyration being greater in the non-dominant hemisphere. In male, but not feminine, patients with schizophrenia, this distinction was reversed. Commissural Changes the commissures (corpus callosum and anterior commissure) are of curiosity in the context of the beforehand talked about work suggesting that hemispheric differences are related to the pathophysiology of psychosis. Witelson and Nowakowski430 instructed that cortical areas which might be more lateralized have fewer interhemispheric connections. This principle has been used within the interpretation of sex variations within the corpus callosum, and the sex difference in age of onset. One can speculate that the sex distinction is by some means associated to the diploma of lateralization in accordance with the Witelson and Nowakowski principle, for instance, that the higher anatomical asymmetry in males reflects greater lack of interhemispheric fibres and perhaps thereby an earlier encounter with a critical threshold of myelination. Using voxel-based morphometry in 159 patients with schizophrenia or schizophreniform disorder and 158 healthy comparability subjects,223 significant decreases in white matter density within the genu and truncus of the corpus of the corpus callosum in left and proper hemispheres and in the right anterior inner capsule and anterior commissure, with no interactions between prognosis and age, were reported. These authors thought-about the findings consistent with aberrant interhemispheric connectivity within the anterior regions of the mind, reflecting decreased hemispheric specialization. A diffusion tensor imaging research of the corpus callosum discovered a rise in mean diffusivity and a decrease in fractional anisotropy within the splenium however not within the genu of the corpus callosum. Gyrification index was reported as decreased on the left aspect in adolescent onset psychosis by Jou et al. Some, however not all, studies have instructed that patients with prominent unfavorable signs have bigger lateral ventricles or progressive ventricular enlargement. This tends to be earlier for males than for females and may explain why males have a more extreme course of the disease. This change in ventricular dimension is accompanied by a modest discount (around 2 per cent) in mind volume and weight, along with comparable reductions in cerebral hemisphere volume, weight and size, whole temporal lobe quantity and size, and superior temporal, fusiform and parahippocampal gyrus volumes. All of those reductions are small in dimension and the gyral changes are likely to be extra marked on the left aspect. A variety of findings have Cortical Gyrification If schizophrenia is a disorder of the cerebral cortex and is developmental in origin, abnormalities of sulcogyral construction could additionally be expected, and in accordance with the asymmetry hypothesis, can be differentially distributed to the 2 hemispheres. A frequently reported finding of upward bowing appears likely to mirror ventricular enlargement, and may have added to the problem of defining intrinsic change. Given the issue of age and sex-related change, it seems that no definitive conclusions concerning interhemispheric transmission can but be drawn.
References:
|



