Buy cheap zibramax 500 mg lineNascent secretory merchandise may be detected immunohistochemically within the cells virus x trip zibramax 250mg generic. Progestational results on the stroma (known because the decidual reaction) are additionally evident within the early secretory part infection vaginal discharge cheap 250 mg zibramax visa. Nuclear enlargement happens and the packing density of the resident stromal cells increases bacteria 5 kingdoms cheap zibramax 250mg amex, due medicine for uti male buy zibramax 250mg fast delivery, in part, to the increase in quantity of gland lumina and onset of secretory exercise in the epithelial compartment. The basal epithelial glycogen mass is progressively transferred to the apical cytoplasm, and nuclei return to the cell bases. The Golgi equipment turns into dilated and products, together with glycogen, mucin and other glycoproteins, are launched from the glandular epithelium into the lumen by a combination of apocrine and exocrine mechanisms; this activity reaches a most 6 days after ovulation. These secretory changes are considerably much less pronounced in the basal gland cells and the luminal epithelium than in the glandular cell population of the stratum functionalis. There is a notable stromal oedema and a corresponding decrease within the density of collagen fibrils. Decidual differentiation occurs within the superficial stromal cells that encompass blood vessels; this transformation includes nuclear rounding and an increased cytoplasmic quantity, reflecting an increase in and dilation of the rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi systems, and cytoplasmic accumulation of lipid droplets and glycogen. In the early secretory part, the endometrium is identified as a skinny echogenic line, a consequence of specular reflection from the interface between opposing surfaces of endometrium. During the late proliferative section, the endometrium seems as a triple layer: a central echogenic line (due to the apposed endometrial surfaces), surrounded by a thicker hypoechoic practical layer, and bounded by an outer echogenic basal layer. It accommodates quite a few veins and spiral arteries that enter the hilum from the mesovarium and lie within a free connective tissue stroma. Small numbers of cells (hilus cells) with traits similar to interstitial (Leydig) cells within the testis are found in the medulla at the hilum; they could be a supply of androgens. Menopause At the menopause, ovulation ceases and various microscopic adjustments ensue within the ovarian tissues. The stroma becomes denser, the tunica albuginea thickens and the ovarian floor epithelium thins. The uterus, ovaries and vagina endure changes during the menstrual cycle, which normally lasts roughly 28 days. A follicle begins a interval of improvement in the ovary during the first days of the cycle, and matures and ruptures mid-cycle (approximately day 14 of a 28-day cycle) to release a secondary oocyte. The wall of the follicle is then remodeled into the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone (luteal phase). About 10 days after ovulation, the corpus luteum begins to regress, then ceases to perform and is replaced by fibrous tissue. The breakdown of the endometrium that follows this cessation of operate is due to the decreasing levels of progesterone and oestrogen because the corpus luteum degenerates. Initially, the tissue is just 1�2 mm thick and is lined by low cuboidal epithelium. In the stratum compactum, which is next to the free surface, the necks of the glands are only slightly expanded and the stromal cells present a distinct decidual reaction. In the stratum spongiosum, the uterine glands are tortuous, dilated and, finally, only separated from each other by a small amount of interglandular tissue. The stratum basalis, next to the uterine muscle, is thin and contains the information of the uterine glands embedded in an unaltered stroma. Note that growing antral follicles are chosen from cohorts of follicles recruited in earlier cycles. The ten lower panels are histological sections of endometrium at the cycle occasions indicated (low magnification on high and high magnification under in each case). Blood escapes from the superficial vessels of the endometrium, forming small haematomata beneath the surface epithelium (see below). The stratum functionalis, next to the free floor, is shed piecemeal, leaving primarily the stratum basalis, adjacent to the uterine muscle; 65�75% of the thickness of the endometrium could additionally be shed. Blood and necrotic endometrium then begin to appear in the uterine lumen, to be discharged from the uterus by way of the vagina because the menstrual flow, which usually lasts 3�6 days.
500 mg zibramaxPetroianu A 1993 Subtotal splenectomy and portal variceal disconnection in the treatment of portal hypertension antibiotics by class buy generic zibramax 100mg on-line. Petroianu A 2003 Subtotal splenectomy for therapy of retarded growth and sexual improvement associated with splenomegaly medicine for uti boots order generic zibramax. Petroianu A recommended antibiotics for acne order 250 mg zibramax with visa, Petroianu S 1994 Anatomy of gastrosplenic vessels in patients with schistosomal portal hypertension antibiotics zithromax purchase discount zibramax on-line. Re G, Casali A, Cavalli D et al 1985 Morphological bases of splenic circulation in congestive splenomegaly. A description of the tortuosity of the splenic artery, demonstrating its significance in anatomical and surgical approaches. Tarantino G, Scalera A, Finelli C 2013 Liver-spleen axis: intersection between immunity, infections and metabolism. Trubel W, Turkof, E, Rokitansky A et al 1985 Incidence, anatomy and territories supplied by the posterior gastric artery. Trubel W, Rokitansky A, Turkof, E et al 1988 Correlations between posterior gastric artery and superior polar artery in human anatomy. Golden yellow in colour, every gland possesses two functionally and structurally distinct areas: an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The glands are surrounded by perinephric fats enclosed within the renal fascia, and separated from the kidneys by a small amount of fibrous tissue. The mean most width of the body of the suprarenal gland is sixty one mm (right) and 79 mm (left), and the mean width of every limb of the gland (medial and lateral) is approximately 30 mm. No particular person suprarenal limb should measure more than 5 mm in transverse part. In adults, each suprarenal gland weighs approximately 5 g (the medulla contributes about one-tenth of the entire weight) and has a quantity of approximately 3�6 cm3 (Wang et al 2013). The proper is pyramidal in form and has two welldeveloped lower projections (limbs), giving a cross-sectional appearance just like a three-pointed star. The left gland is more semilunar in A Area associated to stomach shape, flattened in the anteroposterior plane and marginally bigger than the proper. The bulk of the proper suprarenal sits on the apex of the proper kidney and normally lies slightly greater than the left gland, which lies on the anteromedial facet of the upper pole of the left kidney. At birth, the glands are proportionately bigger and are approximately one-third the dimensions of the ipsilateral kidney. The suprarenal cortex (specifically the fetal zone) reduces in size instantly after birth and the medulla grows comparatively little. By the tip of the second postnatal month, the burden of the suprarenal has decreased by greater than 50%. The glands start to develop again by the top of the second 12 months and regain their weight at start by puberty. They are also sometimes discovered within the spermatic twine, epididymis or testis in boys (Altin et al 1992), and ovary or broad ligament of the uterus in women. Its inferior floor or base overlaps the anterosuperior side of the higher pole of the proper kidney, with the two decrease projections (limbs) of the gland straddling the renal tissue. The anterior surface has two distinct facets: a slender medial facet that lies posterior to the inferior vena cava, and a triangular lateral side that lies in contact with the bare area of the liver. Here, the gland lies posterior to the lateral border of the second part of the duodenum. Below the apex, near the anterior border of the gland, the right suprarenal vein emerges from the hilum to join the inferior vena cava. This vein is short, which makes surgical resection of the gland or mobilization of the inferior vena cava probably hazardous. It may be inadvertently avulsed from the inferior vena cava throughout surgical procedure or, often, by high-energy deceleration accidents. The posterior floor of the gland is divided into upper and lower areas by a curved transverse ridge. The large higher area is barely convex and abuts the diaphragm, whereas the small decrease area is concave and lies in contact with the superior aspect of the upper pole of the best kidney. The medial border of the gland is thin and lies lateral to the best coeliac ganglion and the proper inferior phrenic artery the place the artery runs over the right crus of the diaphragm. The superior border is sharply outlined while the inferior surface is extra rounded.
Effective zibramax 500 mgContraction of quadriceps femoris antimicrobial chemotherapy purchase zibramax with mastercard, therefore infection quizlet buy discount zibramax 100 mg line, tends to displace the patella laterally bacteria 5 letters 100mg zibramax free shipping, which is resisted by the geometry of the joint and by the ligaments antibiotic resistant uti in pregnancy purchase zibramax line. Vastus medialis obliquus acts medially and posteriorly as much as it acts proximally, and so its tension helps to resist the Q-angle impact. This ligament is the only most important stabilizer of the posterolateral area of the knee and resists lateral rotation of the tibia on the femur. Failure to recognize and reconstruct damage to this ligament and to the associated ligamentous constructions is the commonest cause for a poor outcome from an otherwise well-performed operation for restore of ruptured cruciate ligaments. Fleshy fibres broaden from the inferior limit of the tendon to type a considerably triangular muscle that descends medially to be inserted into the medial two-thirds of the triangular area above the soleal line on the posterior floor of the tibia, and into the tendinous growth that covers its surface. An additional head may arise from the sesamoid bone within the lateral head of gastrocnemius. Popliteus minor runs from the posterior floor of the lateral tibial condyle, medial to plantaris, to the indirect popliteal ligament. Peroneotibialis runs deep to popliteus from the medial side of the fibular head to the higher finish of the soleal line. Gastrocnemius, plantaris, the popliteal vessels and the tibial nerve all lie posterior to the enlargement. The popliteal tendon is intracapsular and is deep to the fibular collateral ligament and the tendon of biceps femoris. It is invested on its deep floor by synovial membrane, and grooves the posterior border of the lateral meniscus and the adjoining part of the tibia earlier than it emerges inferior to the posterior band of the arcuate ligament. There are additional contributions from the nutrient artery of the tibia (from the posterior tibial artery), the proximal a half of the posterior tibial artery, and the posterior tibial recurrent artery. Actions Popliteus rotates the tibia medially on the femur or, when the tibia is fixed, rotates the femur laterally on the tibia. Its connection with the arcuate popliteal ligament, fibrous capsule and lateral meniscus has led to the suggestion that popliteus may retract the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus throughout lateral rotation of the femur and flexion of the knee joint, thus defending the meniscus from being crushed between the femur and the tibia throughout these actions. The muscle is markedly energetic in crouching, maybe to provide stability as the tibia rotates medially during flexion of the knee. However, the main operate is prone to be provision of dynamic stability to the posterolateral part of the knee by stopping excessive lateral rotation of the tibia, partly by its direct action, but more considerably by tensing the popliteofibular ligament. A superficial arterial network spreads between the fascia and skin across the patella and in the fat deep to the patellar ligament. The vessels concerned are the superior, center and inferior genicular branches of the popliteal artery; descending genicular branches of the femoral artery and descending department of the lateral circumflex femoral artery; circumflex fibular artery; and anterior and posterior tibial recurrent arteries. Medially, this tendon is joined by collagenous fibres arising from the arcuate popliteal ligament; the fibrous capsule adjoining to the lateral meniscus; and the outer margin of the meniscus. They are often incidental findings within the dissection room, or could come to mild in the midst of angiographic examination. Some variations in vascular anatomy could also be symptomatic and may necessitate surgical correction; different variations, while asymptomatic, may influence technical considerations during vascular surgical procedures. Anatomical variations of the femoral, profunda femoris, anterior and posterior tibial and fibular arteries have been described elsewhere in this Section. It descends laterally from the opening in adductor magnus to the femoral intercondylar fossa, inclining obliquely to the distal border of popliteus, the place it divides into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries. This division usually occurs on the proximal end of the interosseous space between the wide tibial metaphysis and the slender fibular metaphysis. The artery is comparatively tethered on the adductor hiatus and again distally by the fascia associated to soleus, and is due to this fact susceptible to harm following knee accidents. It divides right into a department to vastus medialis that anastomoses with the descending genicular and inferior medial genicular arteries, and a department that ramifies on the femur and anastomoses with the superior lateral genicular artery. The superior lateral genicular artery passes underneath the tendon of biceps femoris, pierces the lateral intermuscular septum and divides into superficial and deep branches. The superficial branch provides vastus lateralis and anastomoses with the descending department of the lateral circumflex femoral and inferior lateral genicular arteries, while the deep department anastomoses with the superior medial genicular artery, forming an anterior arch throughout the femur with the descending genicular artery. The superficial branch is vulnerable if the lateral patellar retinaculum is divided surgically.
Purchase generic zibramax canadaThe tubules are lined with columnar ciliated epithelium and are likely to antibiotic resistance lancet buy zibramax 250mg without prescription represent a vestigial remnant of the mesonephros infection kidney failure zibramax 100mg with visa. The ampullae of the vas deferens lie along the medial margins of the seminal vesicles antibiotic yeast infection treatment generic zibramax 500mg without a prescription, while the veins of the prostatic venous plexus lie laterally antibiotic wipes 100 mg zibramax with amex. Each bulbourethral gland consists of several lobules enclosed by a fibrous capsule. The glandular epithelium is columnar, and secretes acidic and impartial mucins into the urethra prior to ejaculation; the secretions primarily havealubricatingfunction. Venous drainage is offered by the vesiculodeferential veins and the inferior vesicalplexus. Likethebulbourethralglands,theysecretemucusinto the lumen of the urethra prior to ejaculation; the secretions have a lubricatingfunction. The rounded base of the glans, the corona, separates the glans from the penile shaft. The glans is roofed by the foreskin (prepuce), which is a free fold of retractable skin attached to the ventral surface of the glans penis, under the corona, at the frenulum. D, An inferior view of the urogenital triangle of a male, with the erectile tissues of the penis indicated with overlays. Shaft the major portion of the penile shaft consists of the paired corpora cavernosa. The outer longitudinal and internal circular fibres of the tunica form an undulating meshwork when the penis is flaccid however turn into tightly stretched on erection. Smooth muscle bundles traverse the erectile our bodies to type endothelium-lined cavernous sinuses, which give the erectile tissue a spongy appearance on gross examination. The corpus spongiosum contains much less erectile tissue than the corpora cavernosa, and is enclosed by a thinner layer of tunica albuginea. The urethra traverses the size of the corpus spongiosum, terminating at a slitlike meatus on the tip of the glans penis, which is, itself, an growth of the corpus spongiosum. Numerous small preputial glands secreting sebaceous smegma line the corona alongside the base of the glanspenis. Therichblood supply to the spongiosum permits safe division of the urethra during stricturerepair. Intermediate venules within the erectile tissue of the corpora cavernosa come up from the cavernous sinuses and drain right into a subtunical capillary plexus. The deep dorsal vein lies within the midline groove between the 2 corpora cavernosa. External genitalia External iliac artery and vein Internal iliac artery and vein Internal pudendal artery and vein nerves and helicine arteries are intimately related to easy muscle. Emissary veins journey between the two layers of the tunica albuginea, and exit the outer layer in an indirect fashion. The outer layer compresses the emissary veins when the penis becomes engorged with blood, preventing venous outflow, and thereby maintains the erection. The resulting distension compresses the emissary veins, preventing venous outflow. The first discernible occasion during ejaculation is contraction of bulbospongiosus, which occurs roughly six times and is underneath somatic control. Parasympathetic stimulation produces vasodilation, whereas sympathetic innervation causes vasoconstriction, contraction of theseminalvesiclesandprostate,andseminalemission. The look of the scrotal pores and skin may vary from clean to rugated, relying on the diploma of contraction of the underlying dartos muscle. Ifuntreated,priapismleads to ischaemia of the corporal easy muscle and irreversible erectile dysfunction. The fats body of the ischio-anal fossa has been removed and gluteus maximus has been incised in order to expose the course of the pudendal nerve and inside pudendal artery. Venous drainage follows the arterial community, and easy arteriovenous anastomosesarecommon.
Zibramax 100 mg without prescriptionOr 99 bacteria buy zibramax 500mg with mastercard, sometimes infection game online buy zibramax with a mastercard, the clot breaks away from its attachment on the atherosclerotic plaque and flows to a extra peripheral department of the coronary arterial tree antibiotics korean buy zibramax with mastercard, where it blocks the artery at that time virus 2014 fall generic zibramax 100 mg on line. A thrombus that flows alongside the artery in this means and occludes the vessel more distally is called a coronary embolus. Many clinicians consider that local muscular spasm of a coronary artery also can occur. In a standard coronary heart, virtually no massive communications exist among the many bigger coronary arteries. When a sudden occlusion occurs in one of the bigger coronary arteries, the small anastomoses start to dilate inside seconds. But then collateral circulate begins to improve, doubling by the second or third day and infrequently reaching regular or almost regular coronary circulate inside about 1 month. When atherosclerosis constricts the coronary arteries slowly over a interval of many years quite than all of a sudden, collateral vessels can develop at the similar time whereas the atherosclerosis turns into more and more extreme. Therefore, the person might never expertise an acute episode of cardiac dysfunction. Eventually, however, the sclerotic process develops beyond the bounds of even the collateral blood supply to present the needed blood flow, and typically the collateral blood vessels themselves develop atherosclerosis. Myocardial Infarction Immediately after an acute coronary occlusion, blood move ceases in the coronary vessels past the occlusion apart from small quantities of collateral circulate from surrounding vessels. Soon after the onset of the infarction, small quantities of collateral blood begin to seep into the infarcted space, which, mixed with progressive dilation of local blood vessels, causes the realm to turn into overfilled with stagnant blood. Simultaneously the muscle fibers use the last vestiges of the oxygen within the blood, causing the hemoglobin to become totally deoxygenated. Therefore, the infarcted area takes on a bluish-brown hue, and the blood vessels of the area seem to be engorged regardless of lack of blood circulate. In later levels, the vessel walls turn into extremely permeable and leak fluid; the local muscle tissue becomes edematous, and the cardiac muscle cells start to swell due to diminished mobile metabolism. In comparison, about 8 milliliters of oxygen per one hundred grams are delivered to the conventional resting left ventricle each minute. The purpose for that is that the subendocardial muscle has a higher oxygen consumption and extra difficulty acquiring enough blood circulate because the blood vessels within the subendocardium are intensely compressed by systolic contraction of the heart, as explained earlier. Therefore, any situation that compromises blood move to any space of the heart normally causes injury first within the subendocardial areas, and the harm then spreads outward toward the epicardium. Therefore, a lot of the pumping force of the ventricle is dissipated by bulging of the area of nonfunctional cardiac muscle. When the heart turns into incapable of contracting with adequate pressure to pump sufficient blood into the peripheral arterial tree, cardiac failure and death of peripheral tissues ensue because of peripheral ischemia. This situation, called coronary shock, cardiogenic shock, cardiac shock, or low cardiac output failure, is discussed more totally in the next chapter. Cardiac shock virtually all the time happens when more than 40 p.c of the left ventricle is infarcted, and demise occurs in more than 70 p.c of sufferers once cardiac shock develops. Damming of blood in the veins typically causes little problem during the first few hours after myocardial infarction. Instead, symptoms develop a few days later for the following purpose: the acutely diminished cardiac output results in diminished blood move to the kidneys. Then, for causes which are mentioned in Chapter 22, the kidneys fail to excrete sufficient urine. Consequently, many sufferers who seemingly are getting along well during the first few days after the onset of coronary heart failure will suddenly experience acute pulmonary edema and sometimes will die within a couple of hours after the appearance of the initial pulmonary symptoms. In many individuals who die of coronary occlu- sion, death occurs because of sudden ventricular fibrillation. The tendency for fibrillation to develop is very nice after a big infarction, but fibrillation can sometimes occur after small occlusions as properly. Indeed, some sufferers with continual coronary insufficiency die suddenly of fibrillation without having any acute infarction. Fibrillation is most likely to happen during two particularly harmful intervals after coronary infarction. Fibrillation also can happen many days after the infarct however is less prone to happen then. Acute loss of blood provide to the cardiac muscle causes rapid depletion of potassium from the ischemic musculature. This additionally increases the potassium concentration in the extracellular fluids surrounding the cardiac muscle fibers.
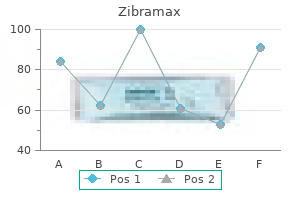
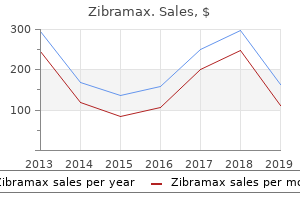
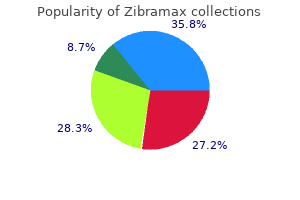
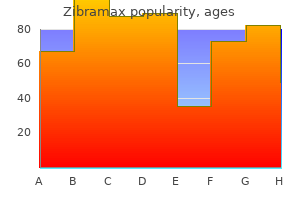
Royal Jasmine (Jasmine). Zibramax. - Are there safety concerns?
- What is Jasmine?
- How does Jasmine work?
- Dosing considerations for Jasmine.
- Liver problems such as hepatitis and cirrhosis, stomach pain due to severe diarrhea (dysentery), increasing sexual desire (aphrodisiac), cancer treatment, use as a sedative, and other uses.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96611
Purchase 100 mg zibramax free shippingThe remaining surface of the center virus ebola sintomas purchase zibramax visa, which continues to be polarized antibiotic withdrawal purchase zibramax discount, is represented by the plus indicators antimicrobial or antimicrobial order zibramax 500mg online. Therefore antibiotics for uti azithromycin purchase genuine zibramax online, a meter related with its unfavorable terminal on the world of depolarization and its positive terminal on one of the still-polarized areas, as shown to the best in the figure, information positively. Even this voltage is small compared with the monophasic motion potential of one hundred ten millivolts recorded instantly on the heart muscle membrane. These placements and readings must be studied fastidiously, and the reader should be succesful of clarify the causes of the respective meter readings. Because the depolarization spreads in all instructions by way of the heart, the potential differences proven in the determine persist for only a few thousandths of a second, and the precise voltage measurements may be achieved only with a high-speed recording equipment. Even the lungs, though largely full of air, conduct electrical energy to a surprising extent, and fluids in other tissues surrounding the center conduct electricity even more easily. When one portion of the ventricles depolarizes and due to this fact becomes electronegative with respect to the remainder, electrical current flows from the depolarized space to the polarized space in large circuitous routes, as noted in the figure. This process provides electronegativity on the insides of the ventricles and electropositivity on the outer partitions of the ventricles, with electrical present flowing via the fluids surrounding the ventricles along elliptical paths, as demonstrated by the curving arrows in the figure. If one algebraically averages all of the strains of current circulate (the elliptical lines), one finds that the average present circulate occurs with negativity towards the base of the center and with positivity towards the apex. During most of the remainder of the depolarization course of, present additionally continues to flow in this identical direction, whereas depolarization spreads from the endocardial surface outward by way of the ventricular muscle mass. Then, instantly before depolarization has completed its course via the ventricles, the common path of current flow reverses for about zero. Thus, in regular heart ventricles, present flows from unfavorable to optimistic primarily in the direction from the bottom of the center toward the apex during nearly the complete cycle of depolarization, except at the very finish. The time period "bipolar" implies that the electrocardiogram is recorded from two electrodes positioned on different sides of the heart-in this case, on the limbs. The electrocardiograph in each occasion is represented by an electrical meter in the diagram, although the actual electrocardiograph is a high-speed computerbased system with an digital display. In recording limb lead I, the unfavorable terminal of the electrocardiograph is related to the proper arm and the positive terminal is connected to the left arm. Therefore, when the right arm is negative with respect to the left leg, the electrocardiograph information positively. This configuration signifies that the electrocardiograph data positively when the left arm is adverse with respect to the left leg. This triangle illustrates that the two arms and the left leg type apices of a triangle surrounding the heart. The two apices on the higher a half of the triangle characterize the factors at which the 2 arms connect electrically with the fluids across the heart, and the lower apex is the purpose at which the left leg connects with the fluids. In different phrases, if the electrical potentials of any two of the three bipolar limb electrocardiographic leads are identified at any given instant, the third one could be determined by simply summing the primary two. Note, nonetheless, that the optimistic and adverse indicators of the totally different leads should be noticed when making this summation. Observing the meters within the determine, one can see that lead I records a constructive potential of +0. Electrocardiographic interpretation of these two forms of conditions-cardiac myopathies and cardiac arrhythmias-is mentioned separately in Chapters 12 and thirteen. This electrode is linked to the optimistic terminal of the electrocardiograph, and the unfavorable electrode, called the indifferent electrode, is connected by way of equal electrical resistances to the proper arm, left arm, and left leg all at the similar time, as additionally proven in the figure. Usually six standard chest leads are recorded, separately, from the anterior chest wall, with the chest electrode being positioned sequentially on the six factors proven within the diagram. Because the heart surfaces are close to the chest wall, every chest lead data mainly the electrical potential of the cardiac musculature immediately beneath the electrode. In this sort of recording, two of the limbs are linked through electrical resistances to the unfavorable terminal of the electrocardiograph, and the third limb is connected to the positive terminal. Study the polarity connections to the electrocardiograph to decide the reply to this question.
Syndromes - Bone x-rays
- Urgent need to urinate
- Abdominal MRI
- Constipation severe enough to require part of large bowel to be removed
- Breathlessness with activity
- Unstable chest wall
- Medicines called chelators that remove mercury from the bloodstream
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- Bloody urine (hematuria)
Purchase zibramax 500mg on-lineFor instance antibiotics for sinus infection while pregnant buy zibramax canada, norepinephrine inhibits contraction of clean muscle within the gut but stimu lates contraction of smooth muscle in blood vessels infection knee replacement symptoms purchase zibramax master card. Kauffenstein G antimicrobial resistance order discount zibramax online, Laher I bacteria have dna generic zibramax 250 mg amex, Matrougui K, et al: Emerging role of G protein-coupled receptors in microvascular myogenic tone. In turn, every of these hearts is a pulsatile two-chamber pump composed of an atrium and a ventricle. Each atrium is a weak primer pump for the ventricle, serving to to move blood into the ventricle. The ventricles then provide the primary pumping drive that propels the blood either (1) via the pulmonary circulation by the best ventricle or (2) by way of the systemic circulation by the left ventricle. In this chapter, we explain how the heart operates as a pump, beginning with the special features of cardiac muscle. The atrial and ventricular forms of muscle contract in much the same way as skeletal muscle, except that the period of contraction is for a lot longer. The specialised excitatory and conductive fibers of the heart, nonetheless, contract only feebly as a outcome of they comprise few contractile fibrils; as an alternative, they exhibit either computerized rhythmical electrical discharge within the form of motion potentials or conduction of the action potentials via the heart, offering an excitatory system that controls the rhythmical beating of the heart. Further, cardiac muscle has typical myofibrils that comprise actin and myosin filaments almost similar to these found in skeletal muscle; these filaments lie side by facet and slide during contraction in the same method as happens in skeletal muscle (see Chapter 6). In other methods, nevertheless, cardiac muscle is type of totally different from skeletal muscle, as we shall see. That is, cardiac muscle fibers are made up of many individual cells connected in sequence and in parallel with one another. At every intercalated disc the cell membranes fuse with one another to kind permeable "communicating" junctions (gap junctions) that enable speedy diffusion of ions. Thus, cardiac muscle is a syncytium of many coronary heart muscle cells in which the cardiac cells are so interconnected that when one cell turns into excited, the action potential quickly spreads to all of them. The heart truly consists of two syncytiums: the atrial syncytium, which constitutes the partitions of the two atria, and the ventricular syncytium, which constitutes the walls of the two ventricles. The atria are separated from the ventricles by fibrous tissue that surrounds the atrioventricular (A-V) valvular openings between the atria and ventricles. This division of the muscle of the guts into two useful syncytiums allows the atria to contract a short time ahead of ventricular contraction, which is important for effectiveness of coronary heart pumping. Rhythmicalactionpotentials(inmillivolts)fromaPurkinje fiber and from a ventricular muscle fiber, recorded via microelectrodes. The presence of this plateau within the action potential causes ventricular contraction to final as much as 15 instances as lengthy in cardiac muscle as in skeletal muscle. The fundamental biophysical answers to these questions were presented in Chapter 5, however they advantage summarizing right here as properly. At least two major differences between the membrane properties of cardiac and skeletal muscle account for the extended motion potential and the plateau in cardiac muscle. First, the action potential of skeletal muscle is triggered nearly totally by the sudden opening of enormous numbers of fast sodium channels that allow tremendous numbers of sodium ions to enter the skeletal muscle fiber from the extracellular fluid. These channels are referred to as "fast" channels as a result of they continue to be open for only some thousandths of a second after which abruptly shut. At the tip of this closure, repolarization happens, and the action potential is over within one other thousandth of a second or so. In cardiac muscle, the motion potential is caused by opening of two kinds of channels: (1) the identical voltage activated quick sodium channels as these in skeletal muscle and (2) another totally different population of Ltype calcium channels (slow calcium channels), which are also referred to as calciumsodium channels. During this time, a big amount of both calcium and sodium ions flows by way of these channels to the interior of the cardiac muscle fiber, and this activity maintains a chronic interval of depolarization, causing the plateau in the motion potential. Further, the calcium ions that enter throughout this plateau phase activate the muscle contractile course of, whereas the calcium ions that trigger skeletal muscle contraction are derived from the intracellular sarcoplasmic reticulum. This decreased potassium permeability could result from the excess calcium inflow through the calcium channels just noted. Regardless of the cause, the decreased potassium permeability tremendously decreases the outflux of positively charged potassium ions through the action potential plateau and thereby prevents early return of the action potential voltage to its resting stage. When the cardiac cell is stimulated and depolarizes, the membrane potential turns into extra constructive. Voltagegated sodium channels (fast sodium channels) open and permit sodium to rapidly flow into the cell and depolarize it.
Buy zibramax 500mg on-lineThe anterior part of the tibial collateral ligament is connected to an space roughly 5 cm long and 1 cm wide close to the medial border of the proximal medial floor antibiotic resistant virus in hospitals cheap zibramax 100mg without prescription. The remaining medial surface is subcu taneous and crossed obliquely by the long saphenous vein antibiotic beads for osteomyelitis buy zibramax 250 mg low price. The distal third antibiotics for uti and bladder infections buy genuine zibramax on line, devoid of attachments bacteria definition for kids purchase zibramax on line amex, is crossed in mediolateral order by the tendons of tibialis anterior (lying simply lateral to the anterior border), extensor hallucis longus, the anterior tibial vessels and deep fibular nerve, extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius. On the posterior surface, popliteus is connected to a triangular space proximal to the soleal line, except near the fibular articular facet. Lateral to the tubercle, the posterior tibial vessels and tibial nerve descend on tibialis posterior. Distal to the soleal line, a vertical line separates the attachments of flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior. Nothing is hooked up to the distal quarter of this floor, however the area is crossed medially by the tendon of tibialis posterior travelling to a groove on the posterior facet of the medial malleolus. Flexor digitorum longus crosses obliquely behind tibialis posterior; the posterior tibial vessels and nerve and flexor hallucis longus contact only the lateral a half of the distal posterior surface. The slightly expanded distal finish of the tibia has anterior, medial, pos terior, lateral and distal surfaces. The distal finish of the tibia, when in comparability with the proximal finish, is laterally rotated (tibial torsion). The torsion begins to develop in utero and progresses all through childhood, mainly in the course of the first 4 years of life (Kristiansen et al 2001), until skeletal maturity is attained. Some of the femoral neck anteversion seen in the new child might persist in adult females: this causes the femoral shaft and knee to be medially rotated, which may lead the tibia to develop a compens atory external torsion to counteract the tendency of the ft to turn inwards. Tibial torsion is approximately 30� in Caucasian and Asian populations, however is significantly larger in Africans (Eckhoff et al 1994). The capsule of the ankle joint is connected to an anterior groove close to the articular floor. The groove is customized to the tendon of tibialis posterior, which often separates the tendon of flexor digitorum longus from the bone. More laterally, the posterior tibial vessels, tibial nerve and flexor hallucis longus contact this surface. The lateral floor is the triangular fibular notch; its anterior and posterior edges project and converge proximally to the interosseous border. The flooring of the notch is roughened proximally by a considerable interosseous ligament but is smooth distally and is sometimes covered by articular cartilage. The anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments are attached to the corre sponding edges of the notch. The distal surface articulates with the talus and is wider in front, concave sagittally and barely convex transversely, i. Medially, it continues into the malleolar articular floor, which may prolong into the groove that separates it from the anterior surface of the shaft. Such extensions, medial or lateral or each, are squatting aspects, and they articulate with reciprocal talar sides in extreme dorsiflexion. These options have been used within the subject of forensic medicine to establish the race of skeletal material. Muscle attachments the patellar ligament is hooked up to the proximal half of the tibial tuberosity. Semimembranosus is hooked up to the distal fringe of the groove on the posterior surface of the medial condyle; a tubercle at the lateral end of the groove is the principle attachment of the tendon of this muscle. Proximal fibres of extensor digitorum longus and (occa sionally) fibularis longus are attached distal to this space. Slips of semi membranosus are hooked up to the medial border of the shaft posteriorly, proximal to the soleal line. Semimembranosus is attached to the medial floor proximally, near the medial border, behind the connect ment of the anterior a part of the tibial collateral ligament. Anterior to this space (in anteroposterior sequence) are the linear attachments of the tendons of sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus; these hardly ever mark the bone. Tibialis anterior is attached to the proximal twothirds of the lateral (extensor) floor.
Buy online zibramaxThe cord-like fibular collateral ligament could additionally be felt passing from the apex of the fibular head to the lateral epicondyle of the femur when the knee is flexed and laterally directed strain (valgus force) is applied to the medial side of the knee systemic antibiotics for acne vulgaris order discount zibramax on line. The medial patellar retinaculum may be felt as a flat antibiotics for uti female discount 250 mg zibramax overnight delivery, broad band overlying the medial femoral condyle within the flexed knee treatment for uti medscape buy generic zibramax 500 mg on-line, operating between the midpoint of the medial aspect of the patella and the medial femoral epicondyle antibiotics for acne oily skin buy 500mg zibramax visa. The horizontal gluteal fold marks the upper restrict of the posterior facet of the thigh. The intergluteal cleft, which separates the buttocks inferiorly, begins superiorly on the S3 or S4 vertebrae. The superior border of gluteus maximus begins on the iliac crest 5�7 cm superolateral to the posterior superior iliac spine and runs inferiorly and laterally in course of the apex of the larger trochanter. Its lower border corresponds to a line drawn from the ischial tuberosity, through the midpoint of the gluteal fold, to a degree roughly 9 cm under the larger trochanter. Although gluteus maximus overlaps the ischial tuberosity within the standing place, on sitting, it slides superiorly posterior to the tuberosity, leaving it free to bear weight. Gluteus maximus can be felt to contract when the hip is prolonged against resistance. Both muscular tissues lie in a slight despair superolateral to gluteus maximus and inferior to the anterior portion of the iliac crest and both cross inferiorly to insert into the higher trochanter. They constitute the main abductors of the hip and are demonstrated by asking the subject to stand on one limb. The ipsilateral muscle tissue contract to stabilize the centre of gravity and preserve a relatively horizontal pelvic position. Leg the muscles in the anterior osteofascial compartment of the leg form a delicate prominence over the higher two-thirds of its anterolateral aspect; this prominence is accentuated when the foot is actively dorsiflexed. Immediately superior to the posterior border of the medial malleolus and close to the medial border of the tibia, the tendons of tibialis posterior and flexor digitorum longus can be felt (rather indistinctly) when the foot is actively inverted and plantar flexed. On the lateral facet of the leg, fibularis longus can be seen as a slim ridge following the road of the lateral side of the fibula throughout energetic eversion and plantar flexion of the foot. The shaft of the fibula can solely be palpated indistinctly between its neck and the area above the lateral malleolus. The two heads of gastrocnemius unite to form the inferior borders of the popliteal fossa. The medial head of gastrocnemius descends to a extra inferior stage than the lateral head. Soleus lies deep to gastrocnemius; when tensed, it bulges from underneath the medial and lateral margins of gastrocnemius, particularly on the lateral aspect, and its fleshy belly extends to a extra distal level. Both muscular tissues end inferiorly in the conspicuous calcaneal tendon, which could be palpated between the finger and thumb and followed inferiorly to its insertion into the posterior facet of the calcaneus. It is bounded superiorly by the inguinal ligament and laterally by the straplike sartorius, which may be both seen and felt in a fairly thin and muscular topic when the hip is flexed in the sitting position, whereas the knee is kept extended and the thigh is barely kidnapped and rotated laterally. Sartorius can be traced inferomedially from the anterior superior iliac spine to approximately midway down the medial facet of the thigh; distally, it might be identified as a gentle longitudinal ridge passing in the path of the posterior part of the medial femoral condyle. The adductor group of muscular tissues varieties the cumbersome, fleshy mass on the upper part of the medial thigh. The medial boundary of adductor longus forms the medial boundary of the femoral triangle and could be felt as a distinct ridge when the thigh is adducted in opposition to resistance. At its superior end, its outstanding tendon of origin may be seen and palpated instantly inferior to the pubic tubercle, which is a helpful guide to this bony landmark. The forward convexity of the anterior thigh is attributable to the curvature of the femur lined by the muscle mass of quadriceps femoris. Rectus femoris seems as a raised ridge passing down the anterior aspect of the thigh to the patellar base, when the sitting subject flexes the hip with the knee prolonged. The thick tendon of adductor magnus can be palpated on the distal medial thigh, deep within the indentation shaped between vastus medialis anteriorly and gracilis and sartorius posteriorly. During ankle inversion and extension of the toes, the distinguished tendon of tibialis anterior is visible on the medial aspect of the dorsal foot, passing inferiorly and medially to the medial cuneiform. The tendon of extensor hallucis longus can be identified laterally; the tendons of extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius are further lateral as they pass deep 1330 Surface anatomy to the inferior extensor retinaculum and immediately anterior to the lateral a half of the distal tibia. More distally, the tendons of extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius diverge and may be traced to their insertions. The tendon is visible and palpable posterior to the malleolus when the foot is forcibly plantar flexed and inverted. The tendon of flexor digitorum longus lies immediately posterolateral to that of tibialis posterior.
References:
|